Design and Verification of Fluorescence Detector for Rapidly Acquiring the Bragg Peak Position of Carbon Ion Beam
-
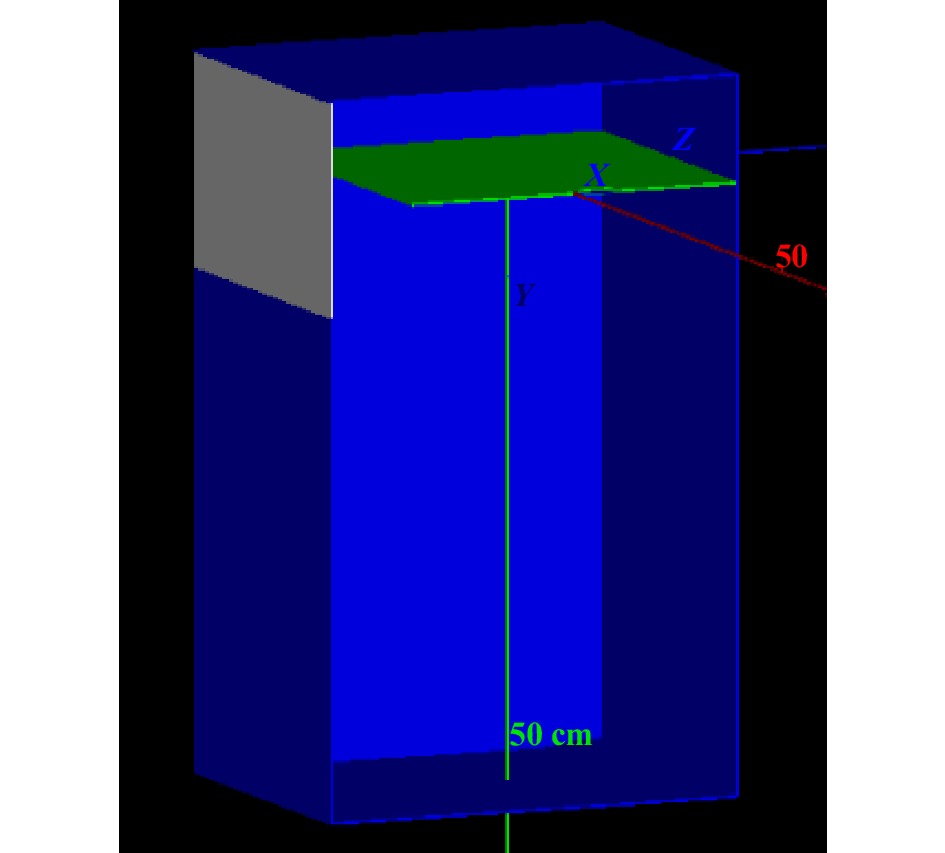
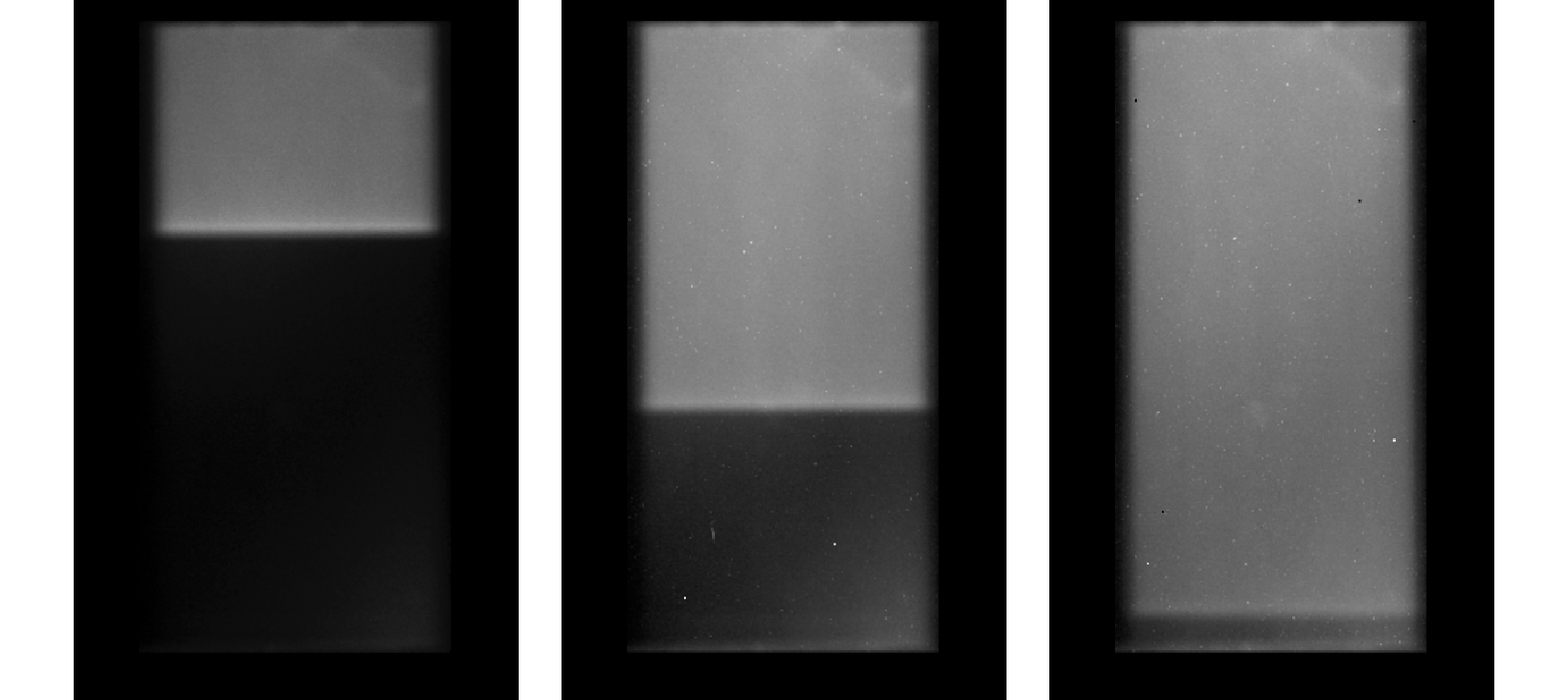
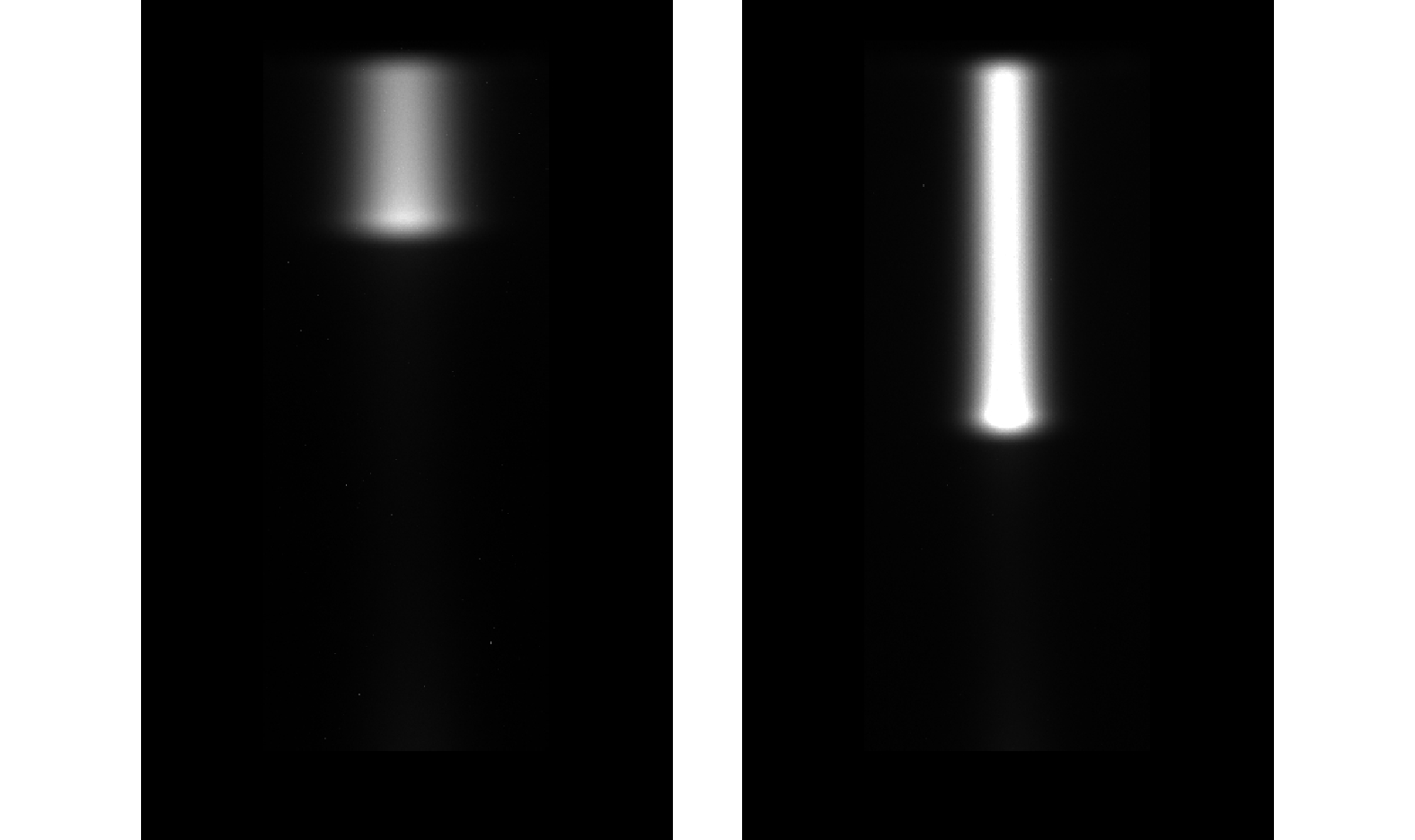
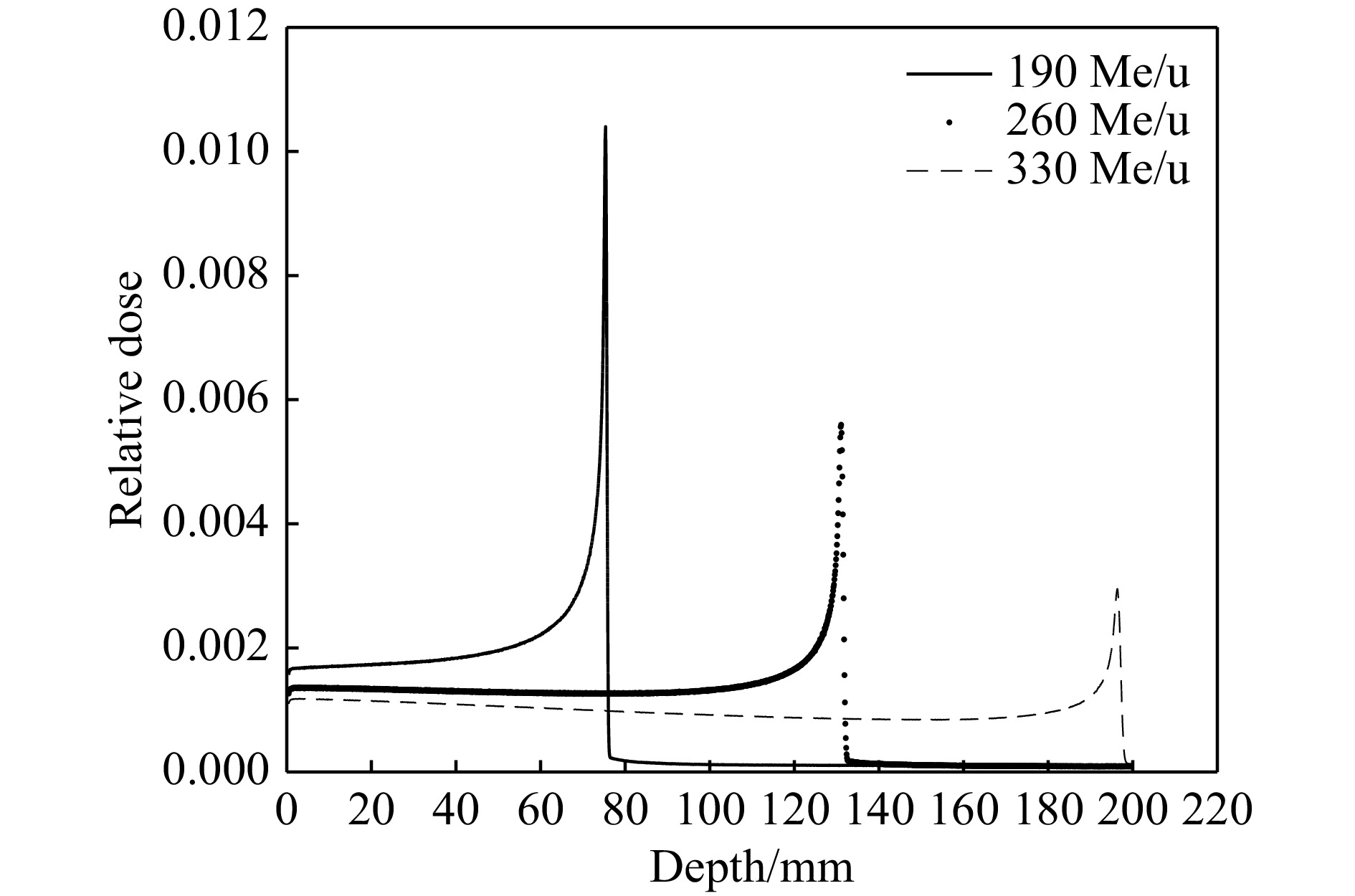
摘要: 提出了一种用于快速获取碳离子束在闪烁体材料中Bragg峰位置的荧光探测器方案。该方案基于闪烁体在碳离子束流照射下发出荧光的特性,使用CMOS相机在薄层闪烁体侧方获得荧光强度分布图像,通过对图像的分析快速得到碳离子束Bragg峰位在闪烁体材料中的位置。依据该方案研发了荧光探测器,在均匀照射野和笔形束两种照射条件下,利用该探测器对不同能量的碳离子束进行了实验测量。实验结果表明,可清晰地从探测器获得的荧光图像上观察到碳离子Bragg峰。同时,采用蒙特卡罗模拟方法对上述相同的实验条件设置进行了模拟计算。结果发现,荧光探测器测量的碳离子束在闪烁体材料中的Bragg峰位与蒙特卡罗模拟计算的结果由于模拟的条件和测量时探测器的实际设置不完全一致而出现一定的差异,但不同照射条件下的差异是基本一致的。因此,通过实验测量及蒙特卡罗模拟验证了本文方案的荧光探测器可用于快速获取碳离子束在闪烁体材料中的Bragg峰位,为建立一种基于荧光探测器进行碳离子放疗束流性能快速质量保证的测量方法打下了坚实的基础。Abstract: A design scheme of fluorescence detector was proposed for rapidly acquiring the Bragg peak position of carbon ion beam in scintillator material. Based on the characteristic of scintillator emitting fluorescence under the irradiation of carbon ion beam, CMOS camera is applied to acquire the image of fluorescent intensity distribution on the side of a thin scintillator, and then the Bragg peak position of carbon ion beam in the scintillator material is quickly obtained by analyzing the fluorescent image. According to the scheme, a fluorescence detector was developed and then used for experimental measurement under the irradiation of carbon-ion uniform fields and pencil beams with different energies. The experimental results showed that the Bragg peak position of the carbon ion beams could be clearly observed from the fluorescent image obtained by the detector. Moreover, the method of Monte Carlo simulation was used to calculate the depth dose distribution of carbon ion beams under the experimental conditions mentioned above. It was found that there was a penetration depth difference between the measured and calculated Bragg peak positions of carbon ion beam in the scintillator material by the fluorescence detector and the Monte Carlo simulation due to the difference between their settings, but the differences under the various irradiation conditions were nearly the same. Therefore, the experimental measurements and Monte Carlo simulations verified that the fluorescence detector scheme could be used for quickly acquiring the Bragg peak position of carbon ion beam in the scintillator material definitely, which provides a substantial basis for establishing a fast fluorescence detector-based quality assurance measurement method in carbon ion radiotherapy.
-
Keywords:
- fluorescent detector /
- Bragg peak /
- Monte Carlo simulation /
- carbon ion therapy /
- quality assurance
-
1. 引言
中子束穿过物体时会发生衰减,当中子入射到物质后,与物质中的原子核相互作用,导致透射后的中子强度及其分布发生变化。因此可以利用中子成像技术,呈现出物质的微观结构信息。中国散裂中子源(CSNS)的设计功率为100 kW,脉冲频率为25 Hz,已于2018年8月向用户开放运行[1]。根据CSNS谱仪发展规划,拟建设一台能量分辨中子成像谱仪(Energy Resolved Neutron Imaging,ERNI),它能结合中子飞行时间实现多参量、多维度、多尺寸信息测量,满足先进材料研发、新能源和器件、装备和部件服役性能和寿命等高新技术产业领域的应用需求[2-4]。
中子敏感微通道板(Neutron sensitive microchannel plate,nMCP)因其具有高的探测效率和位置分辨以及优异的时间分辨能力,配合先进的读出电子学可实现能量分辨中子成像,成为CSNS-ERNI探测器的优先选择。nMCP最早是由Fraser等[5]发明的一种微通道电子倍增器件,常见的MCP具有六边形通道排布的蜂巢结构,通道轴线与法线具有一定的夹角以增加电子倍增概率。普通MCP可以通过基体掺杂和孔道镀膜中子灵敏核素(10B、6Li和natGd)这两种方式实现中子敏感特性,进而制备nMCP。近年来基于nMCP的中子探测器得到了快速发展,美国加州大学伯克利分校课题组[6-8]利用含有10B的氧化物构成玻璃成分制作出基体掺杂型nMCP,在美国散裂中子源(SNS)和英国散裂中子源(ISIS)进行多次实验,采用Timepix芯片作为读出电子学获得约21%的热中子探测效率、约70%的冷中子探测效率以及好于15 μm的空间分辨。国内方面,清华大学的杨祎罡团队[9-10]与北方夜视的潘京生合作对基体掺杂型nMCP探测器进行研究,在采用延迟线读出条件下获得约34%的热中子探测效率和x轴方向65.6 μm、y轴方向63.7 μm的位置分辨。美国NOVA公司最早将镀膜技术应用于MCP的生产,使镀膜技术在nMCP的制备领域成为可能[11]。清华大学的Lu等[12]对镀膜型nMCP探测器的模拟研究发现,当镀膜厚度在0.1~1 μm之间时对热中子达到最高70%的探测效率,同时成功制备了约208 nm厚的ALD-natGd2O3的中子敏感镀膜层,但未对该种类型的nMCP开展实验研究。中国工程物理研究院的Wang等[13]对镀膜型nMCP探测效率进行了模拟,结果显示热中子探测效率可接近60%。
本文主要针对镀膜型nMCP开展蒙特卡罗模拟和理论计算。首先,对掺杂natGd型nMCP的典型中子和伽马信号进行实验研究。然后,介绍镀膜型nMCP的工作原理,通过模拟得到探测效率的二维分布以及探测效率随着孔径、壁厚、倾角和镀膜厚度的变化关系。最后采用重心法对位置分辨进行计算,研究位置分辨与倾角和镀膜厚度的关系。
2. 传统掺杂钆nMCP的技术瓶颈
当前在高通量的中子束流中,往往会伴随很强的伽马背底,而对典型的中子和伽马信号进行研究有助于后端读出芯片的设计和中子伽马甄别(n/
$\gamma $ )的研究。基于以上两点,对掺杂natGd的nMCP开展实验研究,采用北方夜视技术股份有限公司南京分公司(北方夜视)生产的直径50 mm、厚度0.6 mm、孔径10 μm、壁厚2 μm、倾角8° 并掺杂3%natGd的nMCP,以及直径50 mm、厚度0.5 mm、孔径12 μm、壁厚2 μm、倾角7° 的普通MCP,双片堆叠形成“V-Stack”使用。CSNS是由一台80 MeV负氢直线加速器、一台1.6 GeV快循环质子同步加速器将质子加速至1.6 GeV后轰击钨靶产生散裂中子,经慢化器、中子导管等将强度约为107 n/(cm2·s)的热中子束流引入BL20号束线。如图1(a)所示,束流出口的中子束流经单色器偏转45°后入射至nMCP探测器,在双片MCP电压–1987 V条件下,根据飞行时间的方法使用示波器采集阳极板输出的典型中子和$\gamma $ 信号进行分析。如图1(b)所示,示波器采集的典型中子和$\gamma $ 信号经数据处理后得到中子信号约35 mV、$\gamma $ 信号约39 mV,且中子和$\gamma $ 信号的宽度几乎相近。针对二者信号特征,一方面我们可以针对信号特征设计nMCP探测器后端读出芯片,另一方面由于中子和$\gamma $ 信号的幅度和宽度相差不大,使得通过信号幅度这一方案来实现n/$\gamma $ 非常困难。对于加速器驱动型的散裂中子源由于$\gamma $ 射线的飞行速度远远大于中子的飞行速度,因此可以考虑采用飞行时间法(TOF)这一方案来实现n/$\gamma $ 。3. 镀膜nMCP的工作原理
基体掺杂方式制作的nMCP会消耗大量的中子灵敏原材料,从而增加nMCP的制造成本。近年来针对镀膜型nMCP的研究逐渐增加,相对于基体掺杂型,镀膜型nMCP具有原材料消耗少、无需氢还原工艺、通道内壁具有高的二次电子发射系数等优点。通过在普通MCP孔道内壁镀膜10B2O3使其具有中子灵敏特性,采用低增益的镀膜10B2O3-MCP与高增益的传统MCP配合使用,期望可以解决n/
$\gamma $ 的问题[14]。图2为镀膜型nMCP的结构,单个nMCP孔道由内到外镀膜顺序为中子敏感层、导电层和二次电子发射层。对于镀膜10B2O3的nMCP,中子探测过程涉及几个独立的级联过程(如图3),各反应道及其分支比如式(1)所示:$$\left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {{\rm{n}}{{\rm{ + }}^{{\rm{10}}}}{\rm{B}}{ \to ^{\rm{4}}}{\rm{He}}\left( {{\rm{1}}{\rm{.8\,MeV}}} \right){{\rm{ + }}^{\rm{7}}}{\rm{Li}}\left( {{\rm{1}}{\rm{.0\,MeV}}} \right){\rm{,}}\;\;\;{{6{\text{%}} }}}\\ {{\rm{n}}{{\rm{ + }}^{{\rm{10}}}}{\rm{B}}{ \to ^{\rm{4}}}{\rm{He}}\left( {{\rm{1}}{\rm{.47\,MeV}}} \right){{\rm{ + }}^{\rm{7}}}{\rm{Li}}\left( {{\rm{0}}{\rm{.83\,MeV}}} \right)}+\\{\rm{ \gamma }}\left( {{\rm{0}}{\rm{.48\,MeV}}} \right){\rm{,\;\;\;94{{\text{%}} }}}\;{\text{。}} \end{array}} \right.$$ (1) 入射中子被中子敏感核素10B吸收产生4He的射程为3.54 μm (1 472 keV)和4.23 μm (1 777 keV),7Li的射程为1.91 μm (838 keV)和2.15 μm (1 014 keV)[15]。次级粒子4He和7Li以相反的方向发射,并以一定的概率穿过导电层、二次电子发射层和nMCP基体进入孔道,在孔道电场的作用下轰击二次电子发射层进行倍增,继而被电子学探测。本文探测效率(P)定义为
$$ P = {P_1} \times {P_2} \times {P_3}, $$ (2) 其中P1是中子被10B俘获的概率,P2是带电粒子穿过导电层、二次电子发射层和nMCP基体进入孔道的概率,P3是带电粒子发生倍增并被电子学探测的概率。
对于中子吸收概率P1满足下式:
$${P_1} = 1 - \exp \left( { - {l_{{\rm{eff}}}}N\sigma } \right),$$ (3) 其中:leff为中子在镀膜层中穿行的有效距离;Nσ为10B的宏观截面。中子与10B反应产生的次级粒子α和7Li由于射程的存在会以反应点为中心呈4π方向发射,二者有一定的概率穿越nMCP基体进入孔道。模拟时认为进入孔道的次级粒子一定会发生倍增并被电子学探测,因此在本文的模拟计算中认为P3=1。
4. 镀膜nMCP的探测效率和位置分辨
4.1 探测效率
本文对于nMCP探测效率和位置分辨的模拟采用Geant4蒙特卡罗模拟软件,Geant4是由欧洲核子中心CERN基于C++语言开发的一套开源的蒙特卡罗模拟软件,它主要用于模拟基本粒子穿过物质时发生的相互作用, 在核科学与技术领域有着广泛的应用[16]。如图4所示,nMCP的模拟包含几何模型构建、物理过程模拟和性能计算三部分。几何模型的建模包含nMCP的直径、厚度、孔径(d)、壁厚(w)、倾角(θ)和镀膜厚度(D),基体材料的选择参考北方夜视,镀膜96%的10B2O3形成nMCP[9]。如图2所示,中子源选择边长为孔径与二分之一壁厚之和刚好覆盖nMCP最小周期垂直入射的六边形热中子源。物理模型选择QGSP_BIC_HP高精度模型,将其电磁过程替换为EMLivemore模型,以增加模拟计算的精确度[16]。探测效率的计算主要涉及的物理过程包括中子俘获和次级粒子进入孔道这两个过程,本文认为10B与中子反应产生的α和7Li进入孔道即可被探测。位置分辨的计算涉及到次级粒子的射程,统计α和7Li进入各个孔道的数目和孔道坐标,根据重心法重建位置。根据探测效率和位置分辨的模拟计算结果改变几何参数进行优化,获得达到最优性能时nMCP的优化几何参数。
在nMCP厚度为0.6 mm时,本文重点研究nMCP的d、w、θ和D参数对探测效率P的影响。如图5(a)和(b)所示,随着D增加、d和w的减小,中子吸收效率P1逐渐增大,然后趋于平稳。这是由于当D增加、d和w减小时,nMCP的镀膜面积占比增大,进而P1概率会随之变大,当D达到2 μm后,P1几乎不再变化。如图5(c)所示,当倾角θ=0°时,由于中子束流垂直nMCP端面入射,此时很多入射中子直接穿过孔道而没有被10B吸收,当θ增大时,P1概率会迅速增大然后趋近于1,此时入射中子几乎全部被中子敏感核素10B吸收。
如图6所示,D增加时P2逐渐减小,此时中子与10B反应产生的4He和7Li以各自的射程沿着相反的方向发射,而D的增加会导致4He和7Li的进孔概率下降,从而会导致P2的下降。图6(a)可以看到,d增加时P2会增加,这是由于在w不变d增加的情况下,nMCP的基体面积占比减小,进而4He和7Li进孔的概率随之增加所致。图6(c)可以得到,θ对于P2的影响较小,这是由于次级粒子是沿着4π空间出射造成的,因此nMCP的倾角θ对其几乎没有影响。
下面分析不同中子吸收位置对P2的影响。如图7(a)、(b)和(c)所示,α、7Li和(α,7Li)出射粒子均在靠近孔道一侧具有高的P2概率,相比于7Li,α具有更广泛的位置分布,这也说明了图6(b)中当D相同时,w对于P2的概率影响较小。D增加时,反而会导致靠近孔壁的一侧概率逐渐下降,此时靠近孔道一侧反应产生的α或7Li很难出射至相邻的孔道,从而会导致总的P2下降。另一方面,由于10B价格较为昂贵,当D增加时会增加nMCP的制作成本。因此合理地控制D既可以控制生产成本又可以提升nMCP的性能。
根据式(2)对P的定义以及图5和图6对P1、P2的模拟结果可知,随着D的增加,nMCP的P存在一个最优值。如图8(a)、(b)和(c),当D为1 μm时,P达到最大值。在同一D下,P会随着d的增加而增加,这是由于此时nMCP的基体面积占比减小,镀膜层反应产生的出射粒子更容易进入相邻的孔道倍增,继而P会随之增加。图8(b)所示,w增加时P减小,这是由于此时中子与10B反应产生的次级带电粒子穿透孔壁进入相邻的孔道的概率降低。由于图5(c)中P1随着θ的从无到有迅速增加,因此会导致图8(c)中P会随着θ的增加迅速增加。
4.2 位置分辨
由于通道倾角的影响,中子的入射位置与中子吸收位置之间存在偏差。同时,中子吸收后产生的4He和7Li具有一定的射程,进入通道倍增后被电子学探测,这一过程会进一步造成位置探测的偏差。本文采用重心法对位置进行重建,根据电荷分布的MCP通道坐标[Cn(x, y)]及电荷量,用各个通道的电荷量为权重对电荷重心进行重建表示入射中子位置。假设有C1, C2···Cn个通道存在电荷数分别为q1, q2···qn,则电荷重心法重建过程如式(4)所示:
$$\begin{aligned}& x = \frac{{{x_1} \times {q_1} + {x_2} \times {q_2} + \cdot \cdot \cdot {x_n} \times {q_n}}}{{{q_1} + {q_2} + \cdot \cdot \cdot {q_n}}} \\ & y = \frac{{{y_1} \times {q_1} + {y_2} \times {q_2} + \cdot \cdot \cdot {y_n} \times {q_n}}}{{{q_1} + {q_2} + \cdot \cdot \cdot {q_n}}} \\ \end{aligned}{\text{。}}$$ (4) 在nMCP厚度0.6 mm、孔径10 μm、壁厚1 μm条件下,本文建立几何模型,讨论θ及D对位置分辨的影响。利用Geant4建立nMCP几何模型时,nMCP倾角方向为x轴方向,因此x轴方向位置分辨会随着θ的变化发生改变。如图9所示,x方向位置分辨随着θ的增加逐渐增加,原因是θ的存在会导致垂直入射的中子束流穿越多个通道产生信号,因此x方向的位置分辨迅速增加。当D增加时,由于中子与10B反应产生的α和7Li穿越多个孔道的概率降低,因此位置分辨会减小。计算结果表明,θ过大会导致位置分辨变差。综合考虑探测效率和位置分辨的模拟结果,当nMCP的几何参数选择镀膜厚度为1 μm、孔径10 μm、壁厚1 μm以及倾角3°,此时可以达到约56%的探测效率和约22 μm的位置分辨。
5. 结论
本文首先对掺杂natGd型nMCP的典型中子和
$\gamma $ 信号开展实验研究,针对信号特征一方面我们可以设计读出芯片,另一方面由于中子和$\gamma $ 信号幅度和宽度相差很小,使得通过信号幅度来实现n/$\gamma $ 这一方案很难实现。采用低增益的10B2O3-MCP与高增益的传统MCP配合使用,期望可以解决n/$\gamma $ 问题。相比于掺杂型,镀膜型nMCP具有高二次电子发射系数、消耗原材料少等优点,选择镀膜型nMCP作为本文的研究对象。然后介绍镀膜型nMCP的工作原理,使用Geant4模拟软件与理论计算的方式对镀膜型nMCP的探测效率和位置分辨进行模拟研究。结果表明,当nMCP的几何参数选择为镀膜厚度1 μm、孔径10 μm、壁厚1 μm和倾角3°时,nMCP具有约56%的探测效率和约22 μm的位置分辨。计算结果对ERNI中子探测器的nMCP几何参数设计具有重要意义。在接下来的工作中,将针对镀膜10B2O3的nMCP探测效率、位置分辨和n/$\gamma $ 等性能开展实验研究,为后续ERNI中子探测器的参数设计提供技术参考。 -
表 1 均匀照射野条件下荧光探测器测量与蒙特卡罗模拟计算的碳离子束Bragg峰位深度对比
能量/(MeV·u−1) 荧光探测器
测量/cm蒙特卡罗
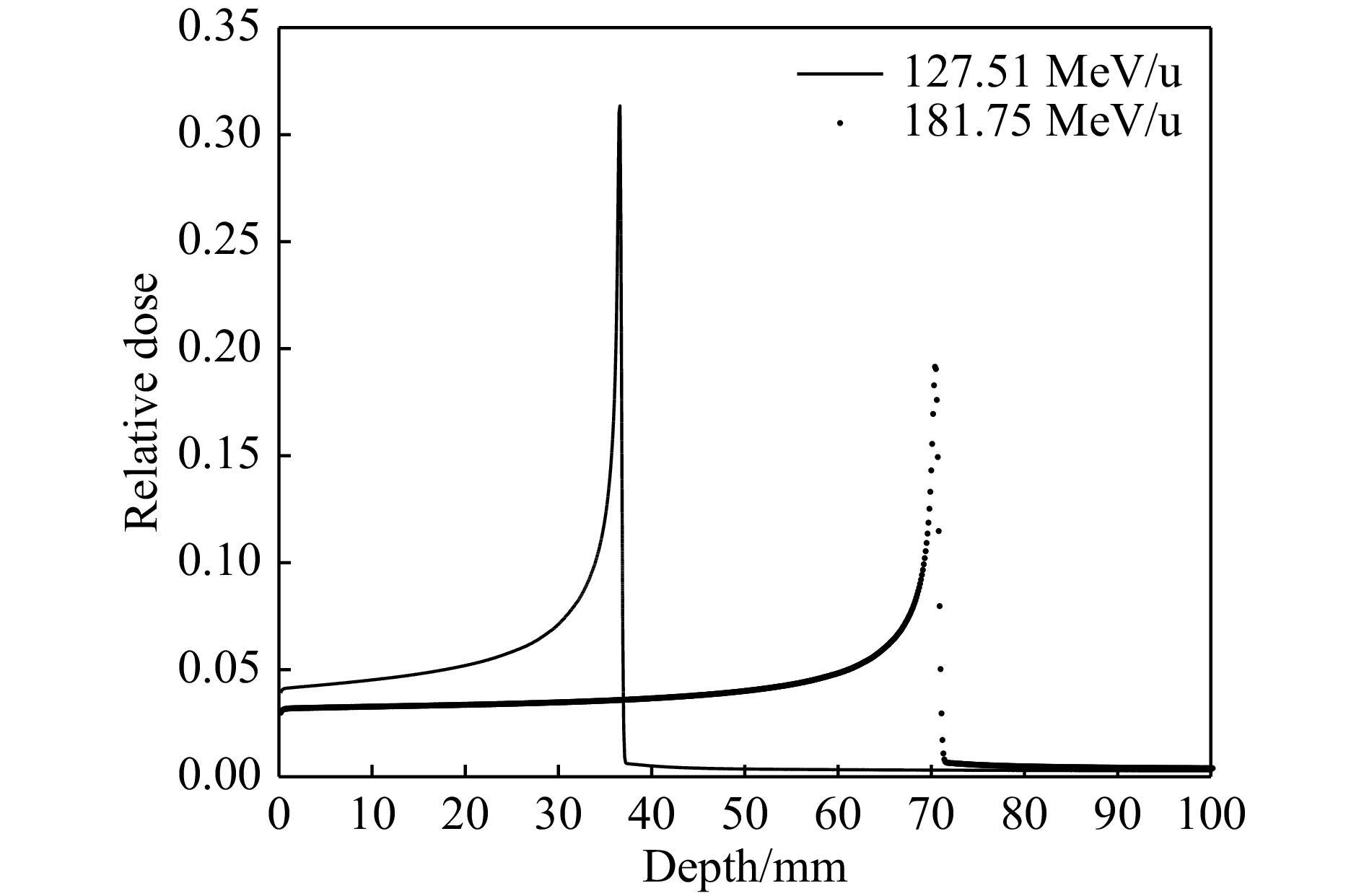
模拟计算/cm差值/cm 190 6.28 7.53 1.25 260 11.86 13.12 1.26 330 18.39 19.68 1.25 表 2 笔形束照射下荧光探测器测量与蒙特卡罗模拟计算的碳离子束Bragg峰位深度对比
能量/(MeV·u−1) 荧光探测器
测量/cm蒙特卡罗
模拟计算/cm差值/cm 127.51 2.40 3.65 1.25 181.75 5.79 7.03 1.24 -
[1] 肖国青, 李强, 张小奇, 等. 科技促进发展, 2020, 16(1): 9. XIAO Guoqing, LI Qiang, ZHANG Xiaoqi, et al. Science & Technology for Development, 2020, 16(1): 9. (in Chinese)
[2] 邓小武. 中国肿瘤, 2008(8): 660. DENG Xiaowu. China Cancer, 2008(8): 660. (in Chinese)
[3] 戴中颖, 李强, 肖国青, 等. 高能物理与核物理, 2007(7): 655. DAI Zhongying, LI Qiang, XIAO Guoqing, et al. High Energy Physics and Nuclear Physics, 2007(7): 655.
[4] ALLISON J, AMAKO K, APOSTOLAKIS J, et al. Nucl Instr and Meth A, 2016, 835: 186. DOI: 10.1016/j.nima.2016.06.125
[5] VISVIKIS D, BARDIES M, CHIAVASSA S, et al. Nucl Instr and Meth A, 2006, 569: 335. DOI: 10.1016/j.nima.2006.08.049
[6] WANG L L, PERLES L A, ARCHAMBAULT L, et al. Phys Med Biol, 2012, 57(23): 7767. DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/57/23/7767
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(2)














 下载:
下载:



















 甘公网安备 62010202000723号
甘公网安备 62010202000723号