-
摘要:
NaI(Tl)晶体是一种常见的辐射探测器材料,由于其与射线相互作用产生的是微弱光信号,因此需要使用光电倍增管将光信号转换为电信号供后级电路处理。硅光电倍增管(Silicon photo-multiplier, SiPM)作为一种新型光电转换器件,相较于传统的光电倍增管具有低噪声、体积小、低功耗和抗磁性等优点。基于SiPM,本工作设计研发了一款1英寸的NaI(Tl)探测器,该探测器具有体积小、本底噪声低的优点,通过优化探测器的物理结构和信号处理电路,实现了对γ射线的高效探测,同时还测试了探测器对137Cs源的能谱影响,结果表明:探测器对0.662 MeV的γ射线能量分辨率为8.72%。
Abstract:The NaI(Tl) crystal is a common material used in radiation detectors. Due to its interaction with radiation, it produces weak light signals, which need to be converted into electrical signals for processing by subsequent circuits using photomultiplier tubes (PMTs). Silicon photomultiplier (SiPM), as a novel type of light-to-electrical conversion device, offers advantages over traditional PMTs, including lower noise, smaller size, lower power consumption, and magnetic field resistance. Based on SiPM, this study designed and developed a 1-inch NaI(Tl) detector. The detector boasts small size and low background noise. Through optimization of the detector’s physical structure and signal processing circuits, efficient detection of gamma rays was achieved. Additionally, the detector’s impact on the energy spectrum of a 137Cs source was tested, revealing an energy resolution of 8.72% for 0.662 MeV gamma rays.
-
Keywords:
- NaI(TI) crystal /
- SiPM /
- Gamma ray /
- high energy resolution
-
0. 引言
γ射线测量技术在环境污染监测、矿源寻找、核事故应急和医学等领域具有重要应用价值[1−4]。近年来,随着核技术的不断进步和发展,高精度γ射线探测器在核科学研究和核工业领域中得到了广泛应用[4]。在放射性探测中,由于γ射线的穿透性强,NaI(Tl)闪烁体探测器因其闪烁效率高、较高的能量分辨率和能谱测量范围广而成为γ射线测量分析的重要工具[5]。传统的NaI(Tl)探测器一般由NaI(Tl)闪烁晶体、光电倍增管(Photo-multiplier tube, PMT)和前置放大器(Pre-amplifier, PA)组成[5],由于这类探测器通常体积较大,且依赖于光电子倍增需求的真空环境,同时其机械性能和抗撞击能力较差,限制了它们在野外、医疗诊断和辐射监测等应用中的灵活性。光电倍增管一直是NaI(Tl)探测器标配的光电传感器,但它们对高压电源(几百伏到几千伏不等)的需求、尺寸较大和易受强磁场干扰等问题限制了便携性和实际应用范围。基于这些问题,近年来,基于硅光电倍增极管(Silicon photo-multiplier, SiPM)的NaI(Tl)探测器引起了广泛的研究兴趣。SiPM作为一种新型的半导体光电转换器件,因其具有噪声低[6]、时间响应快速[6]、偏置电压低[6]、体积小以及对磁场不敏感[6]等优点而被广泛应用用于新型的NaI探测器设计中。本文拟采用蒙特卡罗模拟技术,重点讨论基于SiPM的小型NaI(Tl)探测器的设计和研究方法,包括设计NaI(Tl)探测器的结构尺寸、性能参数设计、制作方法以及在核物理领域中的应用场景。该研究有望改善核辐射监测、医学诊断和核物理研究等领域的性能,为人类健康和环境保护提供更可靠的工具和方法。因此,深入研究和优化这一技术是当前放射性核素测量领域的重要任务。
1. 探测器设计
1.1 选型与模拟设计
1.1.1 晶体选型
闪烁体探测器的探测原理是入射的射线粒子(例如γ)进入闪烁体中,经过光电效应、康普顿散射、电子−空穴对的形成等相互作用,闪烁体发出光子,但由于这些光子微弱无法直接被探测到,故需采用光电倍增管的光阴极将其转换为电子后进行倍增放大,以便电子学仪器采集[5]。因此,发光效率、发光波长、发光衰减时间等参数是晶体选型的重要指标[7]。
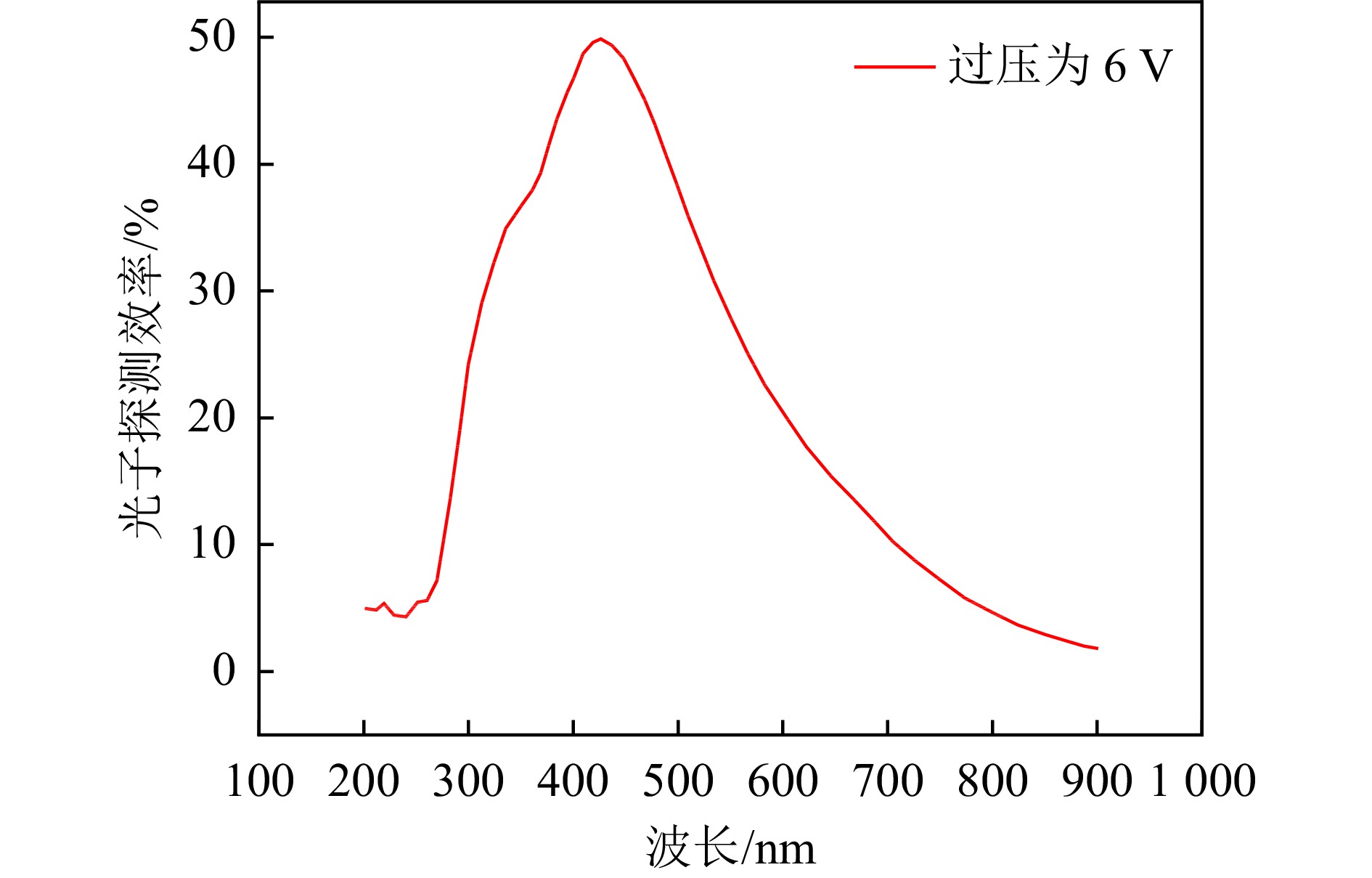
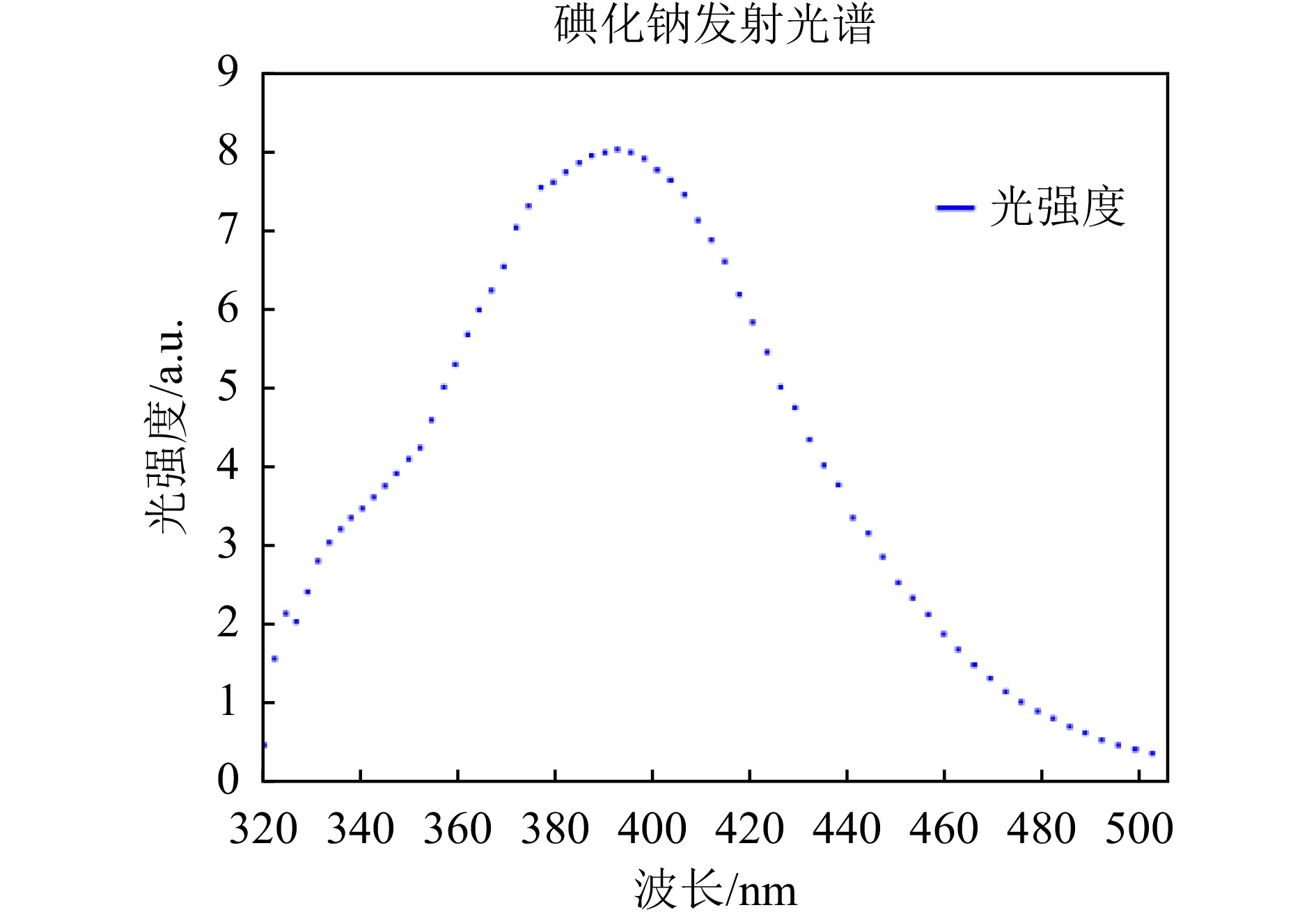
如表1所列,LaBr3(Ce)晶体具有较高的相对光输出,这表明对于同一能量的射线,LaBr3(Ce)可以产生更多的光子。这类晶体的能量分辨率可以达到2.6%~4.2%(137Cs @662 keV),但其价格昂贵,且本身具有放射性, 会干扰辐射测量过程。NaI(Tl)探测器的能量分辨率在7%~9%(137Cs@662 keV),NaI(Tl)闪烁体是伽马射线测量使用范围最广的晶体之一,具有良好的密度特性(3.67 g/cm3);其生产制备工艺成熟,价格低廉易于获得的同时,具有较高的发光效率(38光子/keV)[5];此外,如图1和2所示,SiPM的最佳光谱响应波长(430 nm)与NaI(Tl)发光波长(420 nm)匹配程度较好,SiPM的光子探测效率约30%~40%,其量子效率比PMT好[8],因此采用SiPM耦合NaI(Tl)晶体的探测器可以满足高效探测的设计需求。由于探测器随探测面边长的增加,光子探测效率(Photon detection efficiency, PDE,指一定时间内器件探测到的光子数与入射到器件表面的光子数百分比[8])增加,能量分辨率更高,又考虑到系统的小型化设计,因此NaI晶体尺寸选择边长为1英寸(约2.54 cm)的正方体。
表 1 常见伽马射线探测晶体性能表材料 发射谱极
大值波长/nm发光衰减
时间常数/μs$ {\lambda }_{\mathrm{m}} $折射率 密度/
(g·cm−3)相对光
输出/%NaI(Tl) 420 0.230 1.85 3.67 100 CsI(Tl) 565 0.680(64%) 1.79 4.51 45 LaBr3(Ce) 380 0.016 1.90 5.20 165 1.1.2 探测器的蒙特卡罗模型
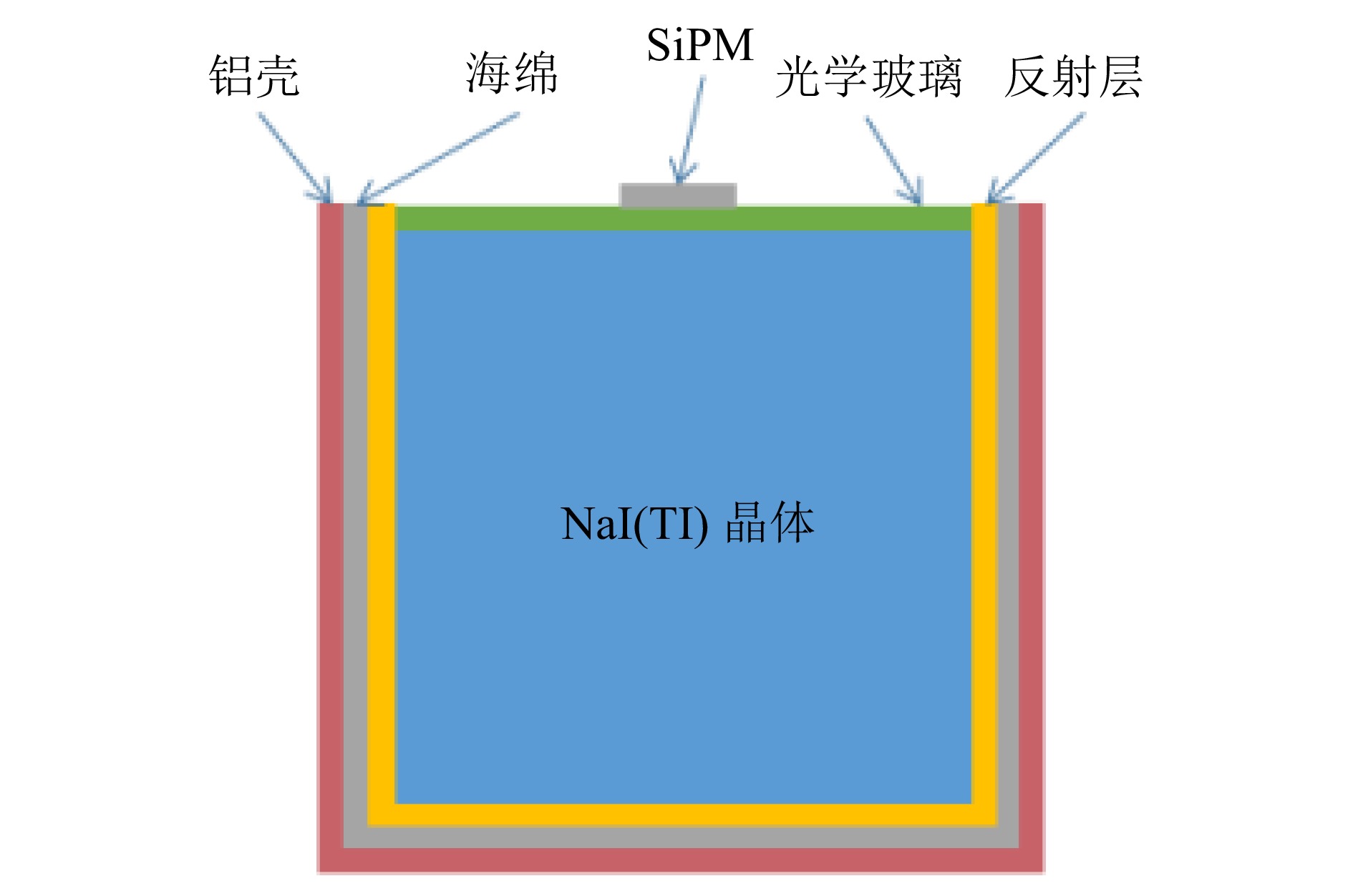
为了验证设计原理, 通过蒙特卡罗(Monte Carlo, MC)模拟方法模拟计算探测器的结构参数,对不同出光面面积在探测面收集到光子数目和能量分辨率进行模拟[9]。图3为NaI闪烁体与SiPM耦合组成的探测器探头部分的示意图。
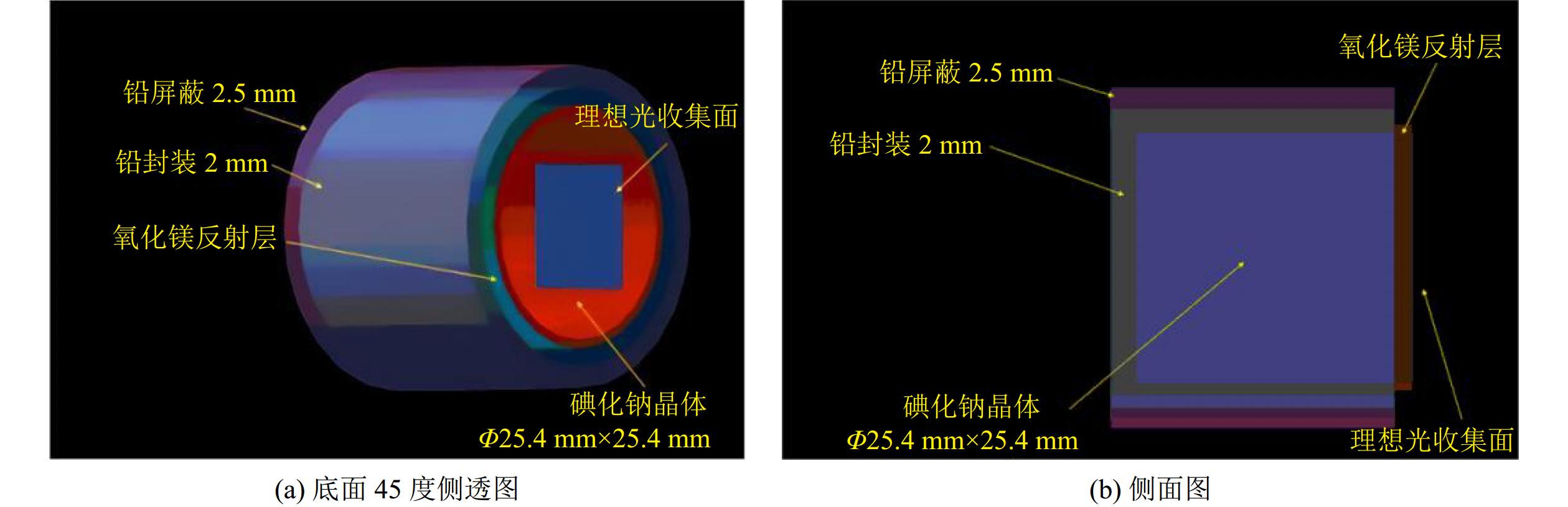
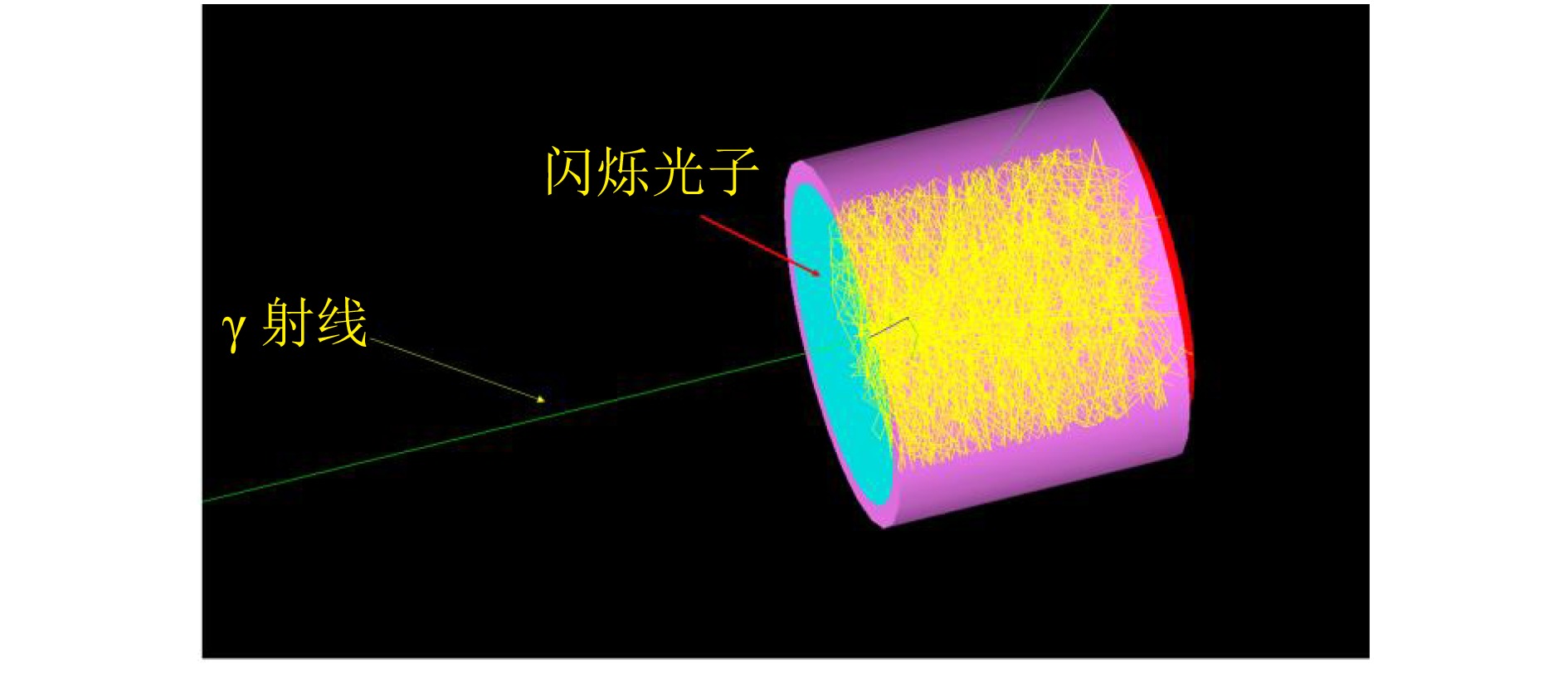
如图4所示,在Geant4中对碘化钠探测器进行建模,碘化钠探测系统主要由铅层、铝层、碘化钠晶体、玻璃光导和探测面组成。这些部件中,铅层用于屏蔽外部本底射线;碘化钠晶体用于吸收γ射线并将射线转化为闪烁光[10];氧化镁反射层用于收集和反射闪烁光子;玻璃光导位于晶体和探测面的中间,连接晶体和探测器,减少空气全反射并使闪烁光子在探测面被收集;探侧面吸收闪烁光子,根据闪烁光子的波长对应的量子效率计算光电子数,并由Geant4程序记录。
$$ R^2=(\delta_{\rm{i}\mathrm{n}})^2+(\delta_{\rm{p}})^2+(\delta_{\rm{s}t})^2+(\delta_{\rm{n}})^2, $$ (1) 其中:$ {\delta }_{\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}} $为闪烁体自身的分辨率,表示闪烁光发射的统计涨落;$ {\delta }_{\mathrm{p}} $为转移分辨率,表示闪烁光输运过程中对能量分辨率的贡献;$ {\delta }_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{t}} $为SiPM的统计贡献,表示探测吸收闪烁光过程中的统计涨落;$ {\delta }_{\mathrm{n}} $为暗噪声的贡献[11]。模型中对闪烁光子在碘化钠探测器中的输运过程进行了模拟,但简化后的理想光收集面不具备模拟电子学器件特性的能力,如暗噪声。因此本研究模型模拟探测器的能量分辨率可经过式(1)简化后得到式(2):
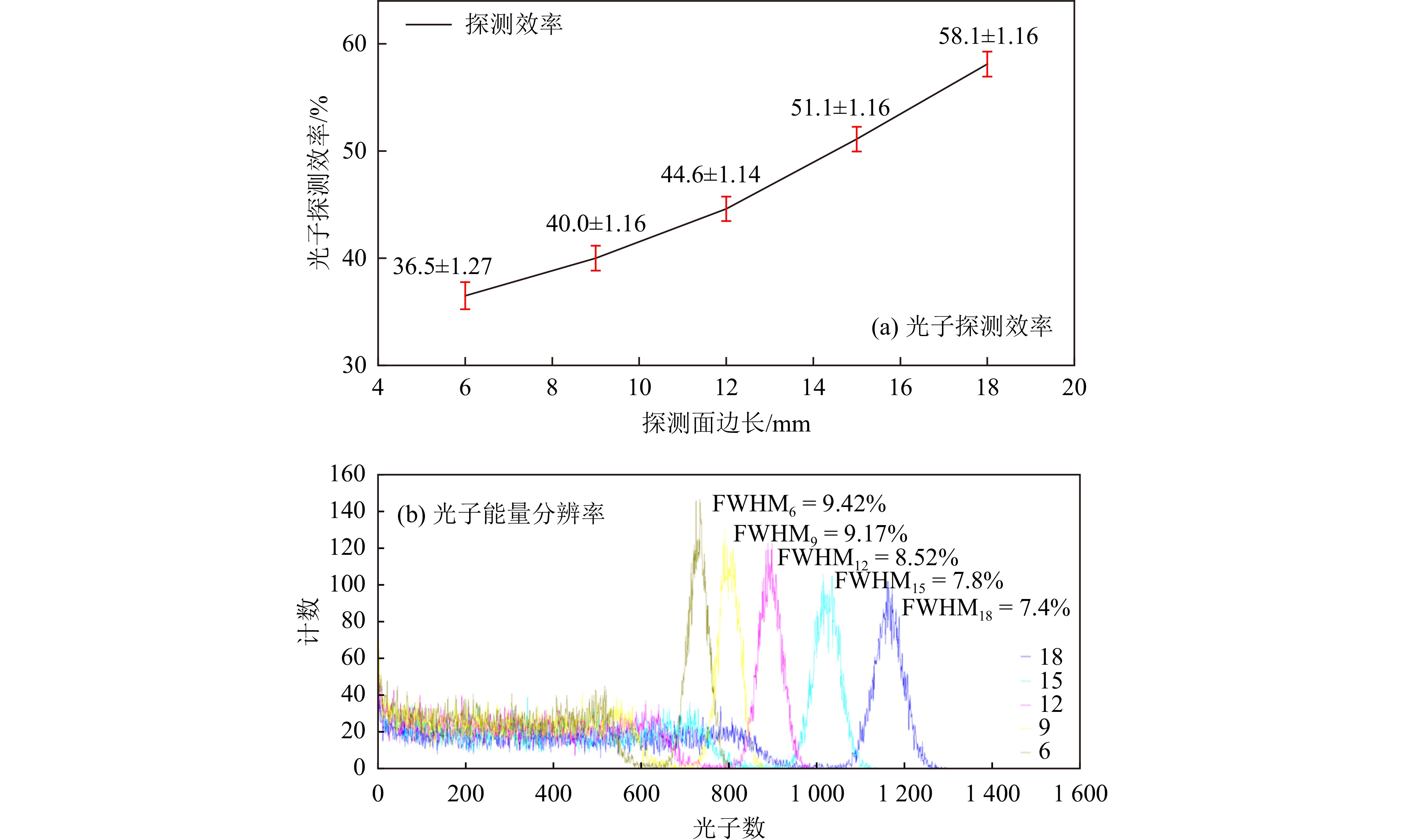
$$ R^2=(\delta_{\mathrm{in}})^2+(\delta_{\mathrm{p}})^2。 $$ (2) 在碘化钠探测器模型中加入光子,可得到闪烁光子的对应发射光谱和输运过程,图5为探测器模型中闪烁光子的输运途径示意图,绿色为γ射线,黄色为闪烁光子。因此本模型可以对闪烁光的统计涨落过程$ {\delta }_{\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}} $进行准确模拟;模型中氧化镁反射层和玻璃光导可对闪烁光子进行反射和折射,因此可以对光子在探测器内部的输运过程$ {\delta }_{\mathrm{P}} $进行准确模拟。由于蒙特卡罗模拟程序无法模拟电子学过程,因此本模型无法模拟$ {\delta }_{\mathrm{n}} $过程,但模型可以对探测器的能量分辨率进行一定程度的预测。由于SiPM的外型为规则立方体,因此在不使用异形光锥的情况下可使SiPM完全落在晶体底面内,本文选用的1英寸碘化钠晶体可耦合边长最大约为18 mm的器件,以18 mm为最大值,3 mm为梯度建立不同尺寸的光收集面的模型,得到不同探测面边长下探测器的能量分辨率。结果显示当探测面截面为正方形时,随着探测面边长增加,探测面对于闪烁光子的探测效率[8]和能量分辨率变化趋势如图5所示。
由图6(a)和(b)可知,随着探测面边长的增加,光子探测效率增加,能量分辨率越好。因为探测面积的增加,不仅可以吸收更多的闪烁光子,提高了测量中的光子探测效率,而且到达出射面附近的光子更可能被探测吸收而不是被折射或反射,因此降低了闪烁光子输运过程中的统计涨落,使能量分辨率提高。为使探测器的能量分辨率达到最佳,同时又兼顾小型化设计的需要,经过多次模拟,得到的碘化钠探测器详细参数如表2所列。
表 2 碘化钠探测器模拟参数部件 尺寸/(mm$ \times \mathrm{m}\mathrm{m}) $) 材料 密度/(g·cm−3) 铅壳 外壁 $ \mathrm{\Phi }30.9\times 25.4 $ Pb 11.35 内壁 $ \mathrm{\Phi }28.4\times 25.4 $ 铝壳 外壁$ \mathrm{\Phi }28.4\times 25.4 $ Al 2.70 内壁 $ \mathrm{\Phi }26.4\times 25.4 $ 氧化镁反射层 外壁$ \mathrm{\Phi }26.4\times 25.4 $ MgO 3.58 内壁 $ \mathrm{\Phi }25.4\times 25.4 $ 碘化钠晶体 $ \mathrm{\Phi }25.4\times 25.4 $ NaI(Tl) 3.67 光导 $ \mathrm{\Phi }25.4\times 2.0 $ SiO2 2.21 探测面 $ 6\times 6 \sim 18\times 18 $ 理想光收集面 / 1.1.3 SiPM选型
SiPM作为一种高分辨率、低噪声、高增益的光敏器件,常用于探测低光强信号或单光子事件,其内部集成了许多(几千到几万)个雪崩二极管(Avalanche Photodiode, APD)和淬灭电阻,称为像素单元,这些单元通常呈阵列状排列,紧密相邻,构成一个大的光敏面积。每个单元是工作在盖革模式下的光电二极管[6],当一个光子击中SiPM的光敏面时,每个像素单元的雪崩二极管上便会产生一个雪崩电流,每个雪崩电流累加之后形成输出信号,其幅度正比于产生雪崩的二极管个数,即正比于吸收的光子数(光子计数器),这种增益机制使SiPM能够检测到弱光信号并提供高信噪比[9]。SiPM的分辨率取决于多个因素,包括像素单元的尺寸、数量、增益、电子噪声等。较小的单元尺寸通常提供更好的空间分辨率,而较多的单元和较高的增益可以提供更好的能量分辨率[8]。为得到最佳的探测效率及能量分辨率需保证晶体发射的光子尽可能多地被SiPM收集,减少光子从出光面泄漏,因此,NaI晶体出光面尺寸需与SiPM感光面尺寸基本相同。市面上的主流商用SiPM由于其内部结构和生产制造工艺的差异导致SiPM的偏置电压差异较大,为满足开发需求,降低设计成本和难度,本文拟采用森美(ONSEMI)公司的型号为MicroFJ-60035-TSV的SiPM作为探测器的光电转换器件,其偏置电压在25.2~30.7 V范围内,具有高光子探测效率和定时分辨率传感器的特性,每片感光面积为6 mm×6 mm,像素间距35 μm,含22 292个像素,工作温度范围−45 ºC~85 ºC,封装尺寸为7 mm×7 mm,为了提高灵敏度,满足该探测器的设计需求,采用4片SiPM,感光总面积为12 mm×12 mm,组成2×2的SiPM阵列作为探测器的光电转换器件。
1.2 探测器硬件设计
1.2.1 探头封装设计
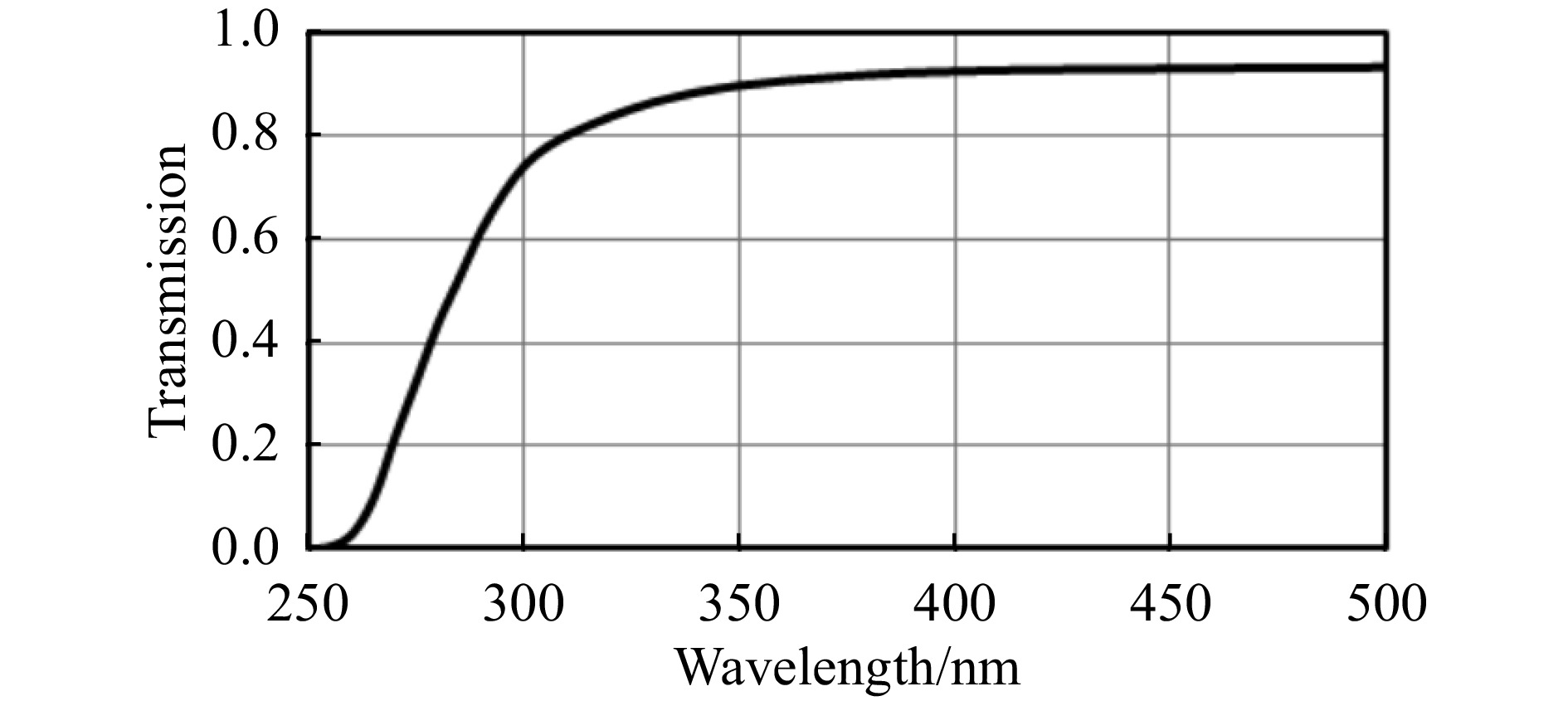
为了提升探测效率,排除闪烁体与SiPM之间的空气,闪烁体与SiPM之间采用光学耦合剂耦合。选用ELJEN Techonology公司生产的专用耦合剂,型号为EJ-560,其具体参数如表3所列,这款耦合剂对NaI(Tl)晶体发射的对应波长范围内的光具有高透明度的特性[11],如图7所示。
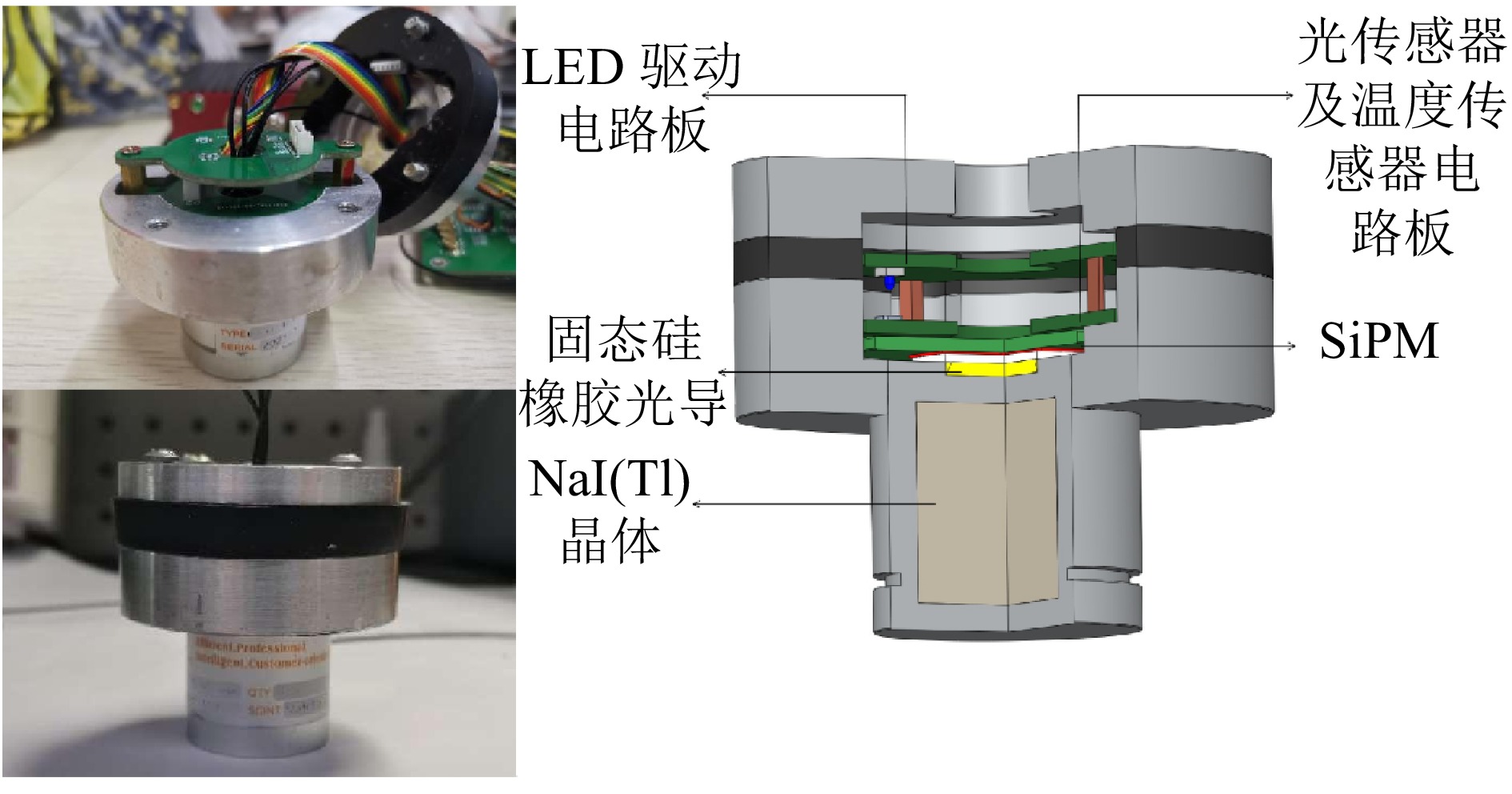
表 3 EJ-560型号光导的具体参数材料特性 密度/(g·cm−3) 邵氏A硬度 折射率 工作温度/ºC 数值 1.03 16~24 1.43 −40~70 由于NaI(Tl)晶体易潮解,虽然出厂时已有防潮处理,但晶体加工存在误差,需进一步进行防潮设计;此外为避免外部光源进入探头对原始信号产生干扰,探头需完全避光,通过在探测器晶体外壳上安装顶盖及橡胶垫片,实现避光防潮,如图8所示。
1.2.2 信号读出及调理电路
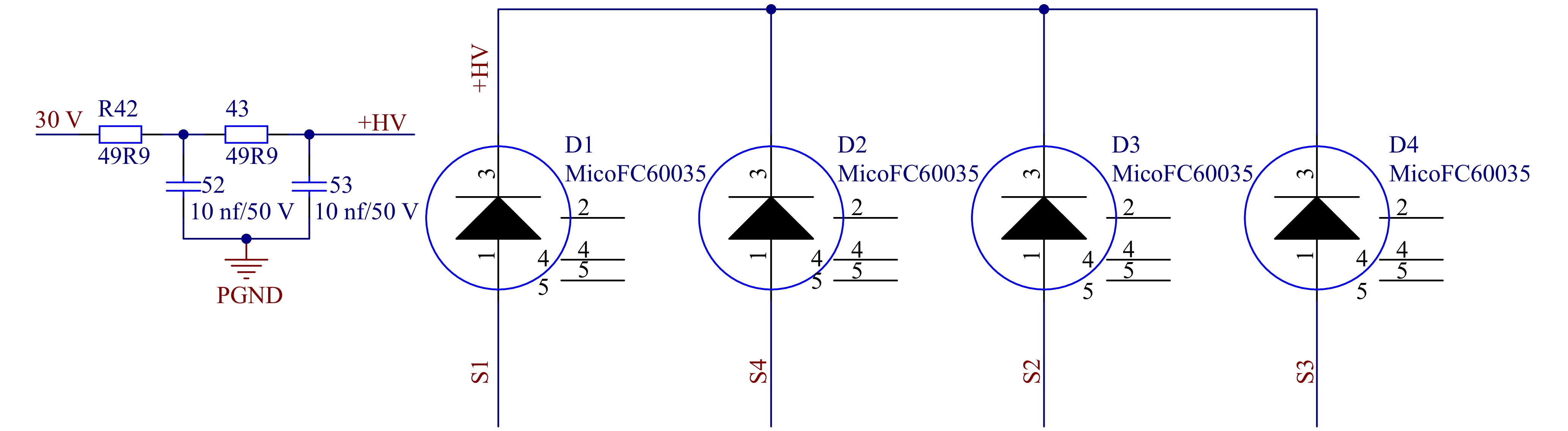
图9所示为探测器信号读出电路。在SiPM的阴极施加29.5 V偏置高压,R42、R43、C52、C53起滤波去耦的作用。
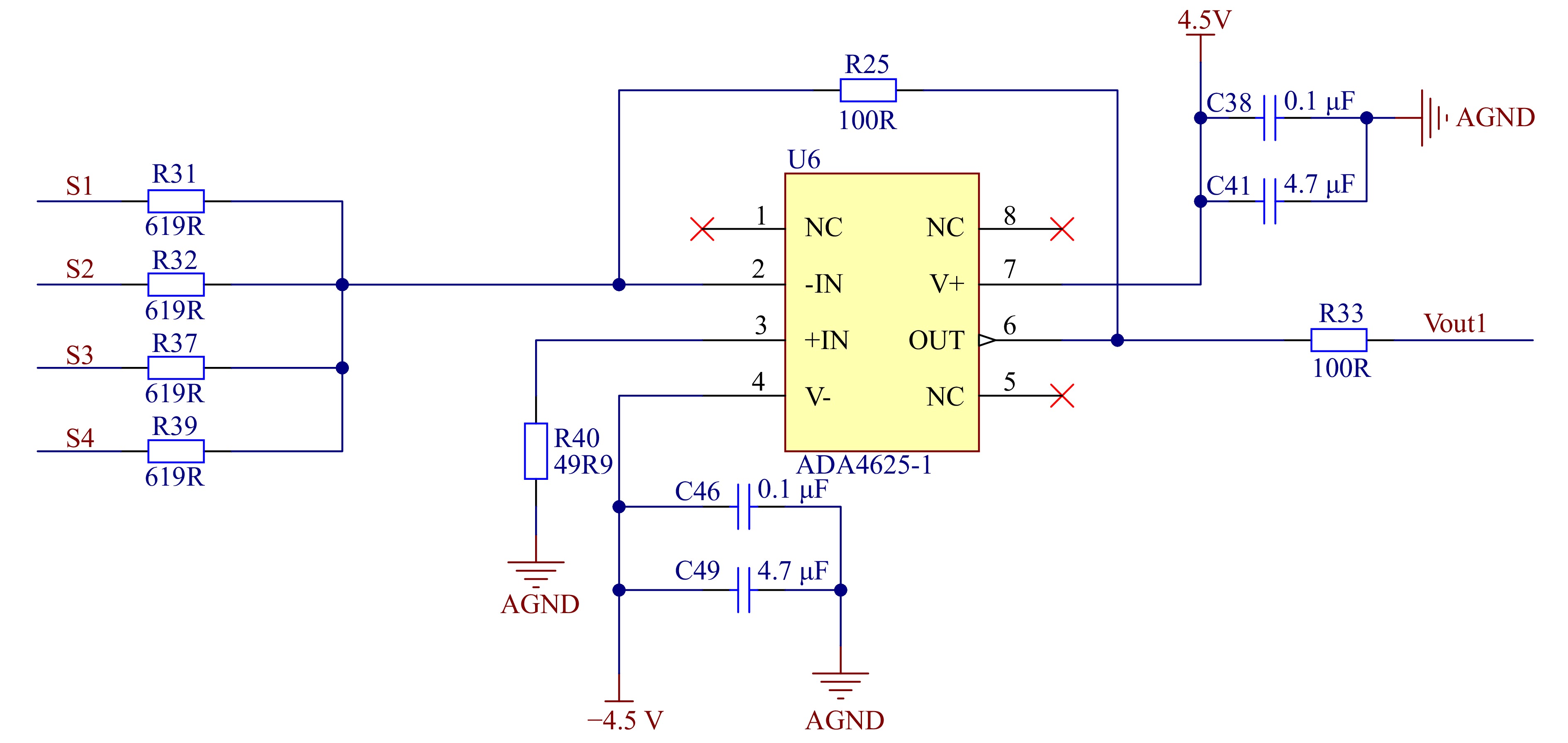
为了使探测器读出的脉冲信号更加清晰直观,采用低噪声运算放大器ADA4625对四个SiPM的输出信号S1、S2、S3、S4进行求和放大,如图10所示。ADA4625是一款低噪声双电源运算放大器,较大的差分输入电压不会引起大的输入电流,标准工况下提供18 MHz增益带宽,低噪声JFET输入[12]和600 Ω负载的驱动能力[13]。SiPM输出的4路信号为正脉冲信号,经过反相求和后,变为为单路负脉冲信号输入至第二级放大电路,输出脉冲幅度为各SiPM输出脉冲幅度之和。
由于数字多道中ADC的输入电压范围在0~2 V,采用ADA4625对前级求和信号二次反向放大,极性变为正脉冲信号,其输出信号与输入的关系可由式(3)得到:
$$ \begin{gathered}V_{\mathrm{o}}-V\mathrm{_i}=\frac{1}{C}\int_{ }^{ }i_{\mathrm{i}}\mathrm{d}t=\frac{1}{C}\int_{ }^{ }\frac{V_I}{R}\mathrm{d}t\text{,} \\ V_{\mathrm{o}}=-\frac{1}{RC}\int_{ }^{ }V_{\mathrm{i}}\mathrm{d}t。 \\ \end{gathered} $$ (3) 为避免运放进入饱和状态,反馈回路中电容并联电阻为充电后的电容提供直流通路共同构成负反馈环回路[14],同时电容起到相位补偿的作用。运放输出脉冲幅度受到电源轨限制,通过配合程控增益电路将信号放大到合适的幅值(0~2 V)进入ADC。运放的正负电源输入端接电容,滤除电源噪声。
1.2.3 电源模块设计
电源模块包括为运放供电的±4.5 V电源和SiPM供电的+29.5 V偏置高压电源。+4.5 V电源采用具有低噪声(3.8 μV)的低压差线性稳压器(Low Dropout Regulator, LDO) TPS7A870,输入电压1.4~6.5 V,输出电压0.8~5.2 V,输出电流500 mA。+4.5 V电源采用反相稳压芯片LM27761,提供高达250 mA的输出电流,运放的静态功耗只有几十mA,可满足运放的功耗需求。
探测器系统采用Sensl公司的型号为Micro-FC-60035的SiPM作为光电转换器件,偏置电压在26~30 V之间,偏压大小影响SiPM的倍增过程,偏压升高,SiPM的灵敏度越高,增益越大[8]。如图11所示,+29.5 V电源采用凌特公司生产的LT8410升压转换器,LT8410采用可变峰值电流和可变关断时间控制方案,并以高开关频率为负载提供高低纹波电压输出[15]。
为实现探测系统增益可控,以实现对不同射线的探测,通过两种方式进行增益调节。
1) 调节SiPM偏置高压
LT8410为SiPM提供偏置电压,其中VREF引脚提供了精确的1.235 V参考电压,VFBP值的大小可由外接电阻调整,输出电压可通过式(4)表示:
$$ V\mathrm{_{out}}=31.85\times V_{\mathrm{FBP}}。 $$ (4) 2) 程控增益
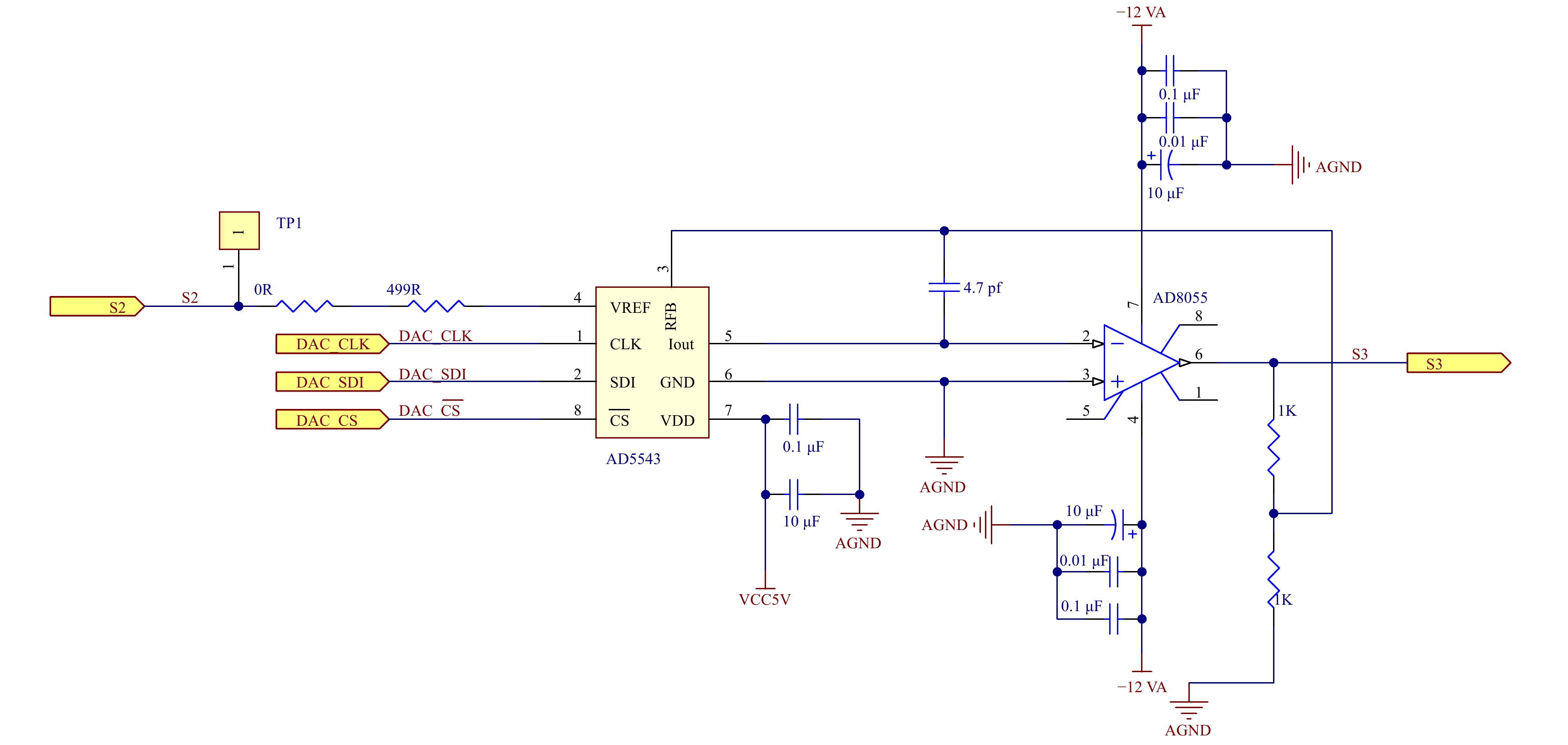
通过DAC器件AD5543调节系统中运算放大器的放大倍数。如图12所示,16位D/A转换器AD5543与运算放大器ADA4817组成增益控制电路,将AD5543的输出端与地分别连接到运放的反、同相输入端,DAC最大输出电流由VREF引脚上所连接的参考电压决定。通过SPI协议向AD5543写入不同值,内部电桥会通过断开或闭合使电路桥两端阻值发生变化,进而改变运放的反馈电阻大小,实现调节放大倍数的目的[16]。
2. 系统分析
2.1 信号测试
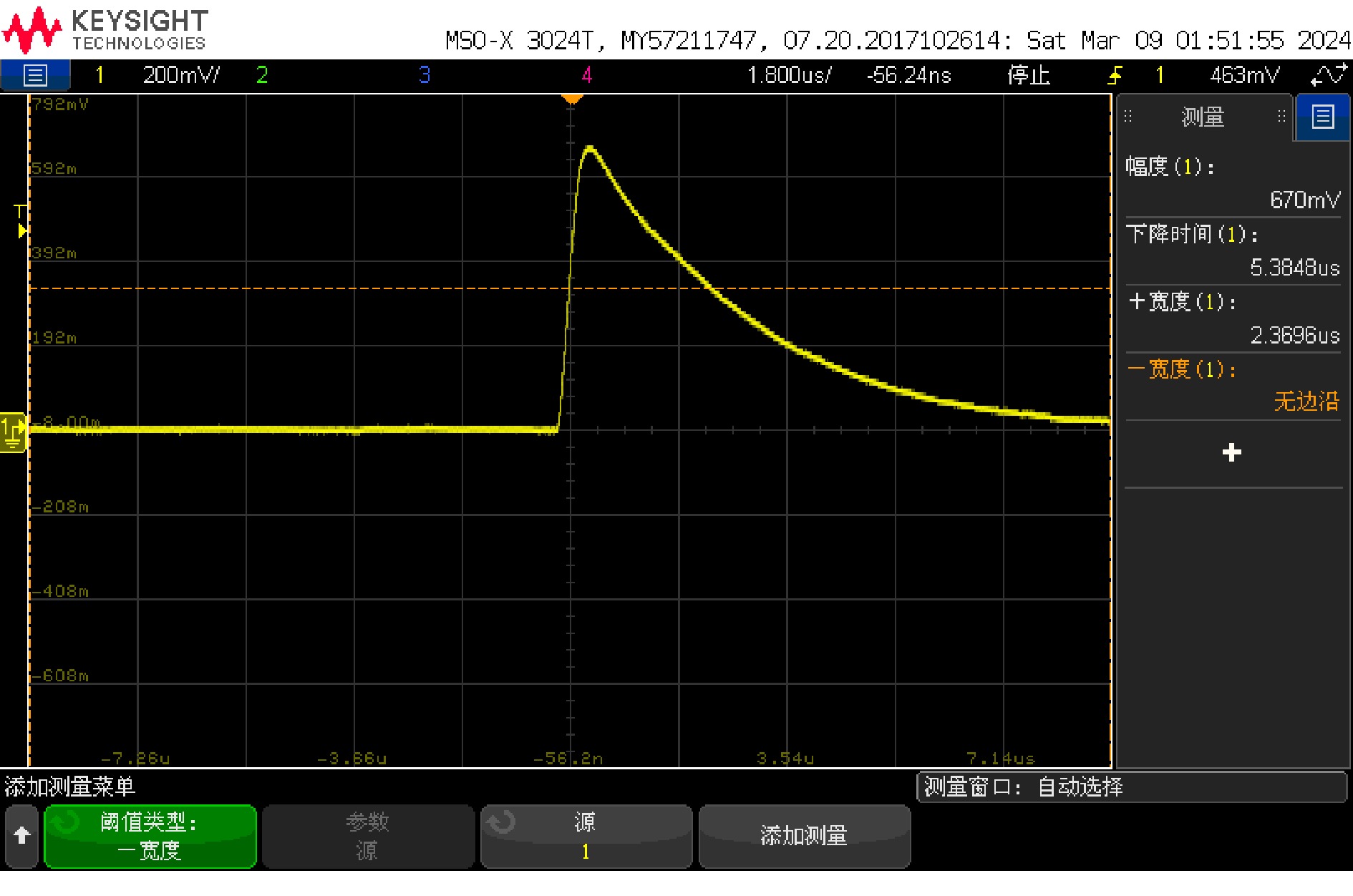
在室温条件下,探测器附近放置一个活度为140 Bq的137Cs点源,测得的前放电路输出的正脉冲信号如图13所示,幅值在670 mV左右,半高处脉冲宽度约为2.37$ {{\mu}}\mathrm{s} $,信噪比约为29.20 dB,该信号可被ADC无失真转换采集。
2.2 电源性能测试
电源的性能一般通过输出电压值和纹波峰-峰值两个参数反映。在室温常压下,输出电压采用4位半的万用表(福禄克15B)测量,电源纹波采用2 GSa/s带宽的示波器(Agilent DSO-X2012A)探针接接地环进行测量,测得输出直流电压和纹波的峰-峰值如表4所列。从表中数据可得,输出直流电压值稳定,噪声均在5 mV以内。
表 4 电源性能测试输出电压值/V 纹波峰-峰值/mV 纹波系数/% +4.49 2.3 0.051 −4.46 2.6 0.058 +29.50 3.3 0.011 2.3 能量分辨率分析
能谱仪的能量分辨率R常用谱线峰的半高宽表示[17],在1.2节中提到影响探测器能量分辨率的因素主要包括:1) 放射源本身的能量分辨率;2) NaI(Tl)晶体的能量分辨率,射线在晶体内损失能量打出荧光光子的过程具有统计涨落特性,这是影响晶体能量分辨率的重要因素,可通过提高晶体的发光效率或者使用更大体积的晶体来实现;3) SiPM对入射光子的光电转换及倍增过程受环境温度、偏置电压、暗噪声以及相邻最小像素单元串扰等因素的影响;4) 电子学系统的影响;因此闪烁体伽马能谱仪的能量分辨率可表示如下:
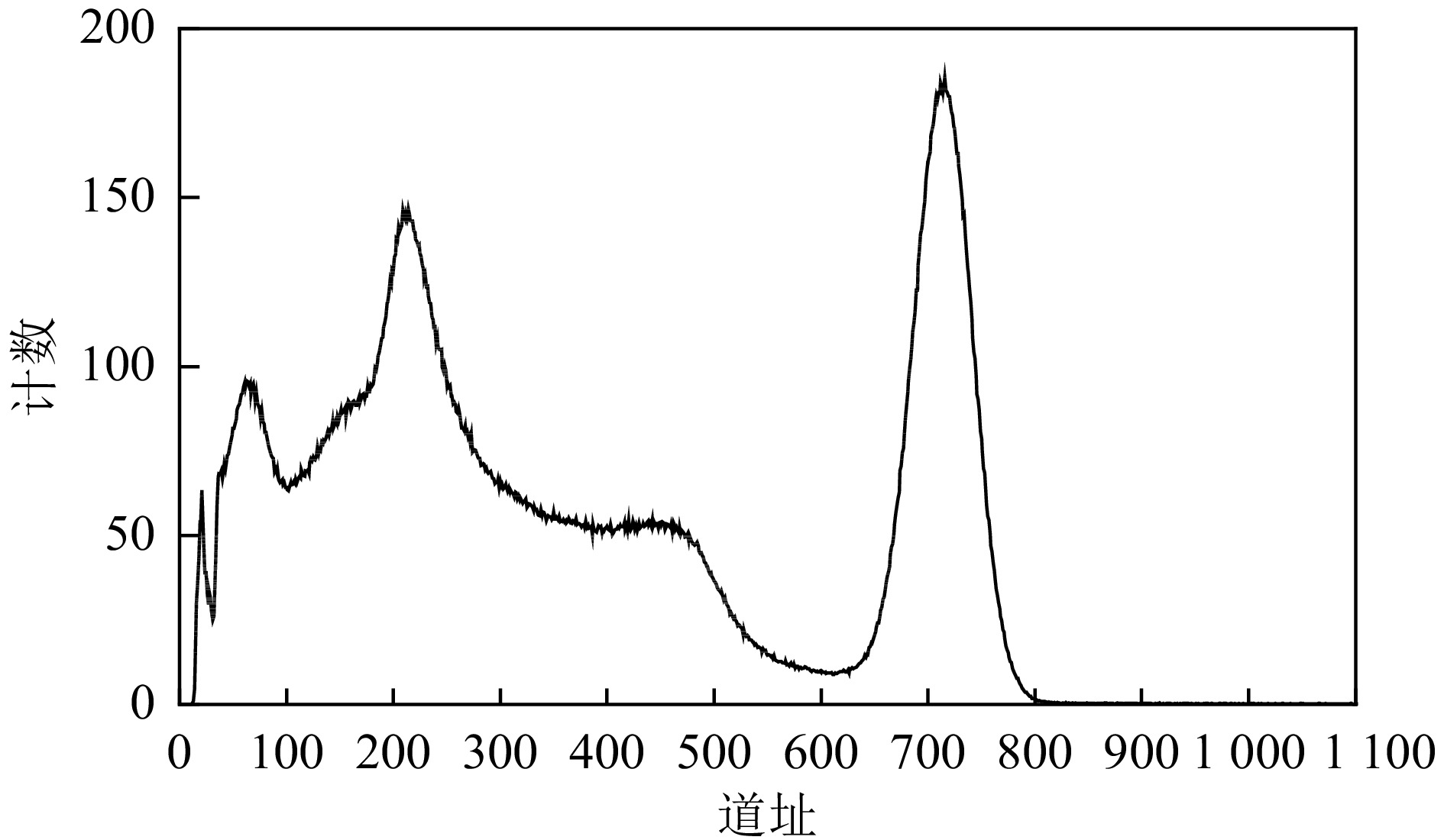
$$ R=\sqrt{R_源^2+R_{\mathrm{NaI(Tl)}}^2+R_{\mathrm{SiPM}}^2+R_{电子学}^2}。 $$ (5) 图14为室温条件下,探测器受137Cs源连续照射5 min后所得能谱情况:此时137Cs全能峰峰位在715道附近,探测器对662 keV大小的射线能量分辨率约为8.72%,测得的能谱本底与高能部分表现良好,高能部分计数低,本底谱线干净,但由于测试环境和测试方法的影响,探测器的能量分辨率会受到影响而变差,其影响因素主要包括:
1) 对于单晶NaI(Tl) γ谱仪来说,能量分辨率是以137Cs的0.662 MeV单能γ射线的光电峰为标准的,一般值在7%~15%,源的不同是影响探测器能量分辨率的一小部分因素。
2) NaI(Tl)闪烁体的影响。铊(Tl)的掺杂浓度对NaI(Tl)的性能和能量分辨率有重要影响。不同的掺杂浓度可能导致不同的光产额和时间响应,进而影响能量分辨率。
3) SiPM的相关噪声。相关噪声是指由先前的光子或暗事件触发的次级雪崩放电的输出,主要分为后脉冲和光学串扰事件。后脉冲主要是APD在雪崩倍增过程中被困在硅中的载流子在APD的恢复阶段被放电,会发生后脉冲。载波最终会产生一个幅度小于原始次级电流的新次级电流脉冲。光学串扰主要是由于一个像素单元中的一次雪崩触发相邻单元中的第二次雪崩所引发的最佳串扰(Optimal Crosstalk, OC),而且光学串扰会随着偏置电压的增加而增加。
4) 电子学引入的噪声,前放电路和信号调理电路中运算放大器等有源器件的噪声和电阻、电容、电感等无源器件会引入噪声,造成探测器的能量分辨率变差。这些噪声主要包括:① 热噪声,即电子元器件中的温度引起的随机电子运动而产生的噪声;② 分布参数线路噪声,即在印刷线路板(Printed Circuit Board, PCB)等分布参数线路中,由于电磁干扰和信号传播的散射,所引入的信号噪声;③ ADC的量化误差引入的噪声;④ 电源噪声,即电源中的电压和电流波动引入的噪声。
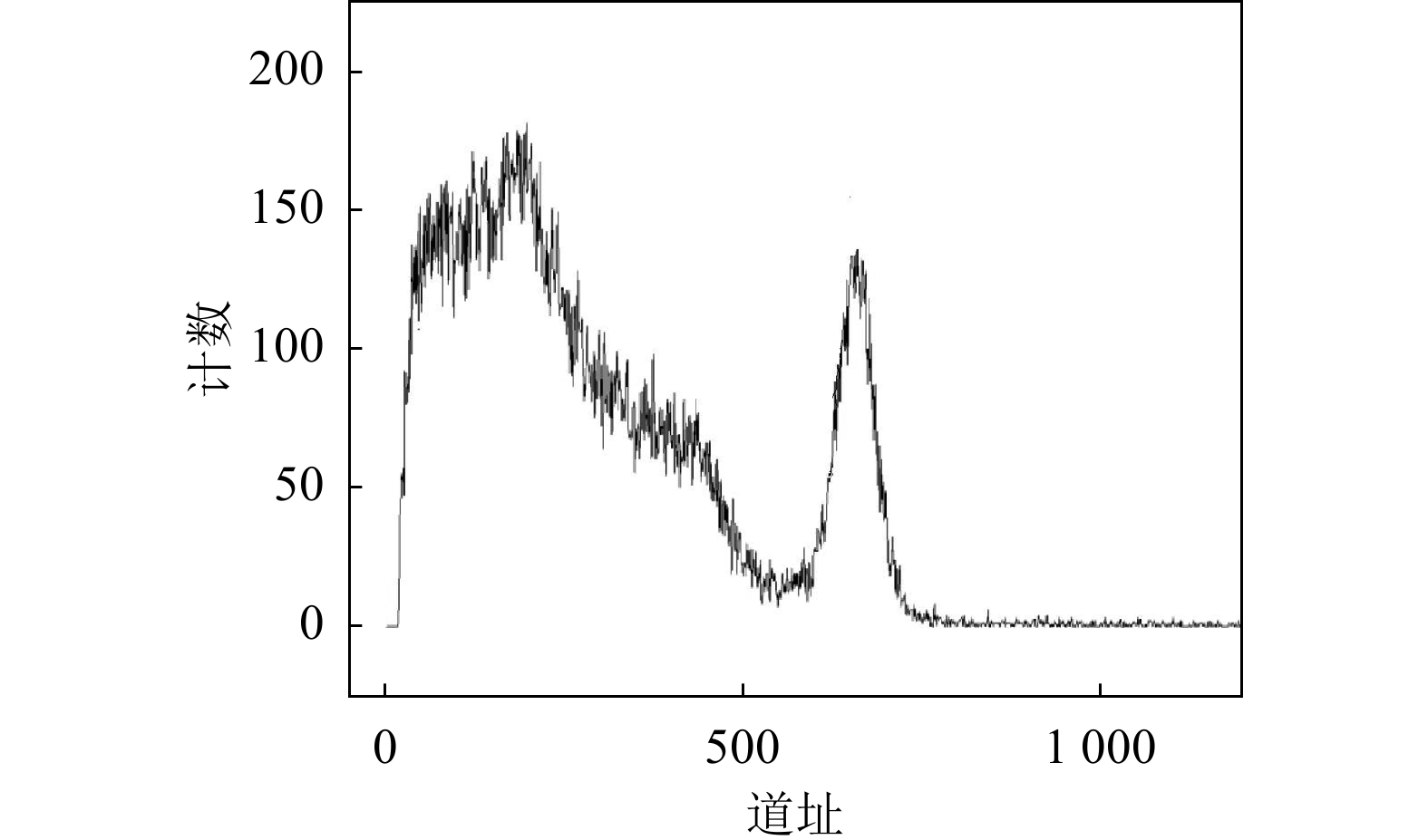
为使实验效果明显,本实验与滨松光子型号为CH249-02的碘化钠探测器的能谱进行对比。滨松光子碘化钠探测器晶体尺寸为直径2英寸、高3英寸的圆柱体,采用R1924A的光电倍增管,脉冲输出幅度在0.6 V左右,采用12 V供电,在同一温度环境下接入与实验相同的探测系统,得到能谱图如图15所示,137Cs全能峰峰位在652道附近,探测器对662 keV大小的射线能量分辨率约为8.82%。由此可得,本实验采用1英寸的NaI晶体和SiPM光电转换器件设计的探测器实现了小型化设计,同时对射线有较好的能量分辨率。
3. 结论
针对小型化SiPM-NaI(Tl)探测器,本文首先在GEANT4平台建立放射源的物理模型和基于闪烁光传输的NaI探测器系统。通过对不同出光面面积在探测面收集到光子数目和能量分辨率进行理论模拟,确定NaI晶体的最佳尺寸。然后设计调试信号读出电路,通过数字多道测得137Cs点源的能谱,并与滨松光子公司NaI闪烁体探测器所测能谱进行比较,结果显示本文设计的SiPM-NaI(Tl)探测器对137Cs(@662keV)射线能量分辨率为8.72%,这表明本实验设计的探测器在保证了较好能量分辨率的同时,又实现了小型化探测器的设计目的。但由于SiPM和模拟电路受温度影响影响较大,这会造成能谱漂移[18]并影响能谱的能量分辨率。因此本文还存在不足,后续将对SiPM信号读出系统的温度效应进行研究,并对其进行温度补偿[19]。
-
表 1 常见伽马射线探测晶体性能表
材料 发射谱极
大值波长/nm发光衰减
时间常数/μs$ {\lambda }_{\mathrm{m}} $折射率 密度/
(g·cm−3)相对光
输出/%NaI(Tl) 420 0.230 1.85 3.67 100 CsI(Tl) 565 0.680(64%) 1.79 4.51 45 LaBr3(Ce) 380 0.016 1.90 5.20 165 表 2 碘化钠探测器模拟参数
部件 尺寸/(mm$ \times \mathrm{m}\mathrm{m}) $) 材料 密度/(g·cm−3) 铅壳 外壁 $ \mathrm{\Phi }30.9\times 25.4 $ Pb 11.35 内壁 $ \mathrm{\Phi }28.4\times 25.4 $ 铝壳 外壁$ \mathrm{\Phi }28.4\times 25.4 $ Al 2.70 内壁 $ \mathrm{\Phi }26.4\times 25.4 $ 氧化镁反射层 外壁$ \mathrm{\Phi }26.4\times 25.4 $ MgO 3.58 内壁 $ \mathrm{\Phi }25.4\times 25.4 $ 碘化钠晶体 $ \mathrm{\Phi }25.4\times 25.4 $ NaI(Tl) 3.67 光导 $ \mathrm{\Phi }25.4\times 2.0 $ SiO2 2.21 探测面 $ 6\times 6 \sim 18\times 18 $ 理想光收集面 / 表 3 EJ-560型号光导的具体参数
材料特性 密度/(g·cm−3) 邵氏A硬度 折射率 工作温度/ºC 数值 1.03 16~24 1.43 −40~70 表 4 电源性能测试
输出电压值/V 纹波峰-峰值/mV 纹波系数/% +4.49 2.3 0.051 −4.46 2.6 0.058 +29.50 3.3 0.011 -
[1] 王庆国, 刘建利, 张岳礼, 等. 陕西地质, 2022, 40(2): 98. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6996.2022.02.017 WANG Qingguo, LIU Jianli, ZHANG Yueli, et al. Shaanxi Geology, 2022, 40(2): 98. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6996.2022.02.017
[2] 王继芳, 徐然, 安茂国, 等. 山东国土资源, 2021, 37(3): 54. WANG Jifang, XU Ran, AN Maoguo, et al. Shandong Land and Resources, 2021, 37(3): 54. (in Chinese)
[3] 杨洁. 核应急中复杂地形场景伽马剂量估算[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2016. YANG Jie. Gamma Dose Estimation for Complex Terrain Scenarios in Nuclear Emergency Response[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2016. (in Chinese)
[4] 翟娟, 赖万昌, 尹楚欧. 电子制作, 2017, (14): 17. DOI: 10.16589/j.cnki.cn11-3571/tn.2017.14.007 ZHAI Juan, LAI Wanchang, YIN Chuou. Journal of Electronics, 2017, (14): 17. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.16589/j.cnki.cn11-3571/tn.2017.14.007
[5] 古再奴尔·安尼瓦, 艾尔肯·阿不列木, 甫尔开提·夏尔丁. 核电子学与探测技术, 2016, 36(11): 1089. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2016.11.002 GUZAINUER·A, AIERKEN·A, PUERKAITI·X. Nuclear Electronics and Detection Technology, 2016, 36(11): 1089. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2016.11.002
[6] 黄土琛, 林少鹏, 王彪. SiPM阵列作为闪烁体读出用于伽马谱仪的研究[C]//中国电子学会, 中国核学会核电子学与核探测技术分会. 第十八届全国核电子学与核探测技术学术年会论文集. [出版者不详], 2016: 8. HUANG Tuchen, LIN Shaopeng, WANG Biao. Research on SiPM Array as Scintillator Readout for Gamma Spectrometer[C]// Chinese Society of Electronics, Nuclear Electronics and Nuclear Detection Technology Branch of Chinese Nuclear Society. Proceedings of the 18th National Nuclear Electronics and Nuclear Detection Technology Annual Conference. [S. l. ], 2016: 8. (in Chinese)
[7] 袁航, 单伟, 赵梦薇, 等. 科技视界, 2021, (10): 90. DOI: 10.19694/j.carolcarrollnkiissn2095-2457.2021.10.28 YUAN Hang, SHAN Wei, ZHAO Mengwei, et al. Science & Technology Vision, 2021, (10): 90. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.19694/j.carolcarrollnkiissn2095-2457.2021.10.28
[8] LIU Jiasong, CAI Hongzhi. Detailed Description of the Performance Parameters of Silicon Photomultiplier Tube[EB/OL][2023-09-08]. http://share.hamamatsu.com.cn/specialDetail/2018.html.
[9] 彭坤涛, 杨羽超, 钟浩威, 等. 能源研究与管理, 2023, 15(1): 184. DOI: 10.16056/J.2096-7705.2023.01.027 PENG Kuntao, YANG Yuchao, ZHONG Haowei, et al. Energy Research and Management, 2023, 15(1): 184. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.16056/J.2096-7705.2023.01.027
[10] 马晓燠, 樊志华, 杨奇龙等. 量子光学学报, 2019, 25(1): 87. MA Xiaoyu, FAN Zhihua, YANG Qilong, et al. Chinese Journal of Quantum Optics, 2019, 25(1): 87. (in Chinese)
[11] MOSZYRISKI M, SWIDERSKI L, SZCZESNIAK T. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2008, 55(3): 125.
[12] 张明敏, 王成鹤, 杨阳, 等. 半导体技术, 2018, 43(2): 115. DOI: 10.13290/j.cnki.bdtjs.2018.02.005 ZHANG Mingmin, WANG Chenghe, YANG Yang, et al. Journal of semiconductor technology, the lancet, 2018, 43(2): 115. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.13290/j.cnki.bdtjs.2018.02.005
[13] Anolog Device Inc. 2017. ADA4625. Low Noise, Fast Settling Single Supply, PRO, JFET Op Amp[EB/OL]. [2023-09-08]. https://www.analog.com/media/cn/technical-documentation/data-sheets/ADA4625-1.
[14] 徐晓光, 黄宏宏, 赵子逸. 廊坊师范学院学报(自然科学版), 2022, 22(2): 26. XU Xiaoguang, HUANG Honghong, ZHAO Ziyi. Journal of Langfang Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 22(2): 26. (in Chinese)
[15] Anolog Device Inc. Linear Technology Corporation Inc. 2008. LT8410. Ultralow power Boost Conventer with output Disconnect[EB/OL]. [2023-09-08]. https://www.analog.com/cn/products/lt8410.html.
[16] Anolog Device Inc. 2012. AD5543. precision 16bit, low power, current output, small form factor digital-to-analog converters (DACs)[EB/OL]. [2023-09-08]. https://www.analog.com/cn/products/ad5543.html#product-overview.
[17] 力茂林, 徐悟生, 张斌, 等. 人工晶体学报, 2023, 52(1): 17. DOI: 10.16553/j.cnki.issn1000-985x.20221206.00 LI Maolin, XU Wusheng, ZHANG Bin, et al. Journal of Artificial Crystal Sinica, 2023, 52(1): 17. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.16553/j.cnki.issn1000-985x.20221206.00
[18] 孙肖南, 孙陶, 李江坤, 等. 计算机测量与控制, 2022, 30(10): 227. DOI: 10.16526/j.carolcarrollnki.11-4762/tp.2022.10.035 SUN Xiaonan, SUN Tao, LI Jiangkun, et al. Computer measurement and control, 2022, 30(10): 227. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.16526/j.carolcarrollnki.11-4762/tp.2022.10.035
[19] 李东, 张雄杰, 王鲍, 等. 电子技术, 2023, 52(4): 9. LI Dong, ZHANG Xiongjie, WANG Bao, et al. Electronic Technique, 2023, 52(4): 9. (in Chinese)




 下载:
下载:

 甘公网安备 62010202000723号
甘公网安备 62010202000723号