Estimation of Equivalent Thermal Neutron Fluence Rate in the Leakage Beam of China Initiative Accelerator Driven System
-
摘要: 加速器驱动次临界系统(ADS)利用质子轰击散裂靶产生的中子驱动次临界堆稳定、持续运行,有望实现长寿命次锕系核素嬗变,并进行洁净能源生产。在加速器与反应堆耦合过程中,束流管道贯穿反应堆的顶盖,堆芯中的散裂中子和裂变中子会通过束流管道大量泄漏,需开展相关屏蔽设计,以减小顶盖外的设备活化,进而减小停堆后堆顶设备维修人员所受辐射剂量。传统热堆的堆外辐射屏蔽设计中,常将热中子注量率限制在105 n/(cm2 · s),以减小设备活化,提高可维护性。对于加速器驱动次临界系统而言,顶盖漏束具有快中子谱、注量率高等特点,需以热中子等效注量率为限值,开展相关屏蔽设计分析。本工作以加速器驱动嬗变研究装置(CiADS)为例,分析了顶盖漏束后产生的活化核素的预期辐射释能,并通过与热中子的预期辐射释能进行等效,得到了束管漏束屏蔽设计所需的漏束中子注量率,并对其适用性进行了评估。研究表明,平均注量率为9.292×105 n/(cm2 · s)的漏束中子在预期辐射释能上等效于注量率为105 n/(cm2 · s)的热中子,在相关辐射屏蔽设计中,可保守取顶盖外部中子注量率限值为8×105 n/(cm2 · s)。本工作提出了一种ADS堆外活化屏蔽设计时的热中子等效注量率的选取方法,可为快谱下的屏蔽分析提供参考。本文获得的热中子等效注量率可用于CiADS顶盖屏蔽的工程设计与分析。
-
关键词:
- 加速器驱动嬗变研究装置 /
- 顶盖屏蔽 /
- 热中子等效注量率 /
- 预期辐射释能
Abstract: The Accelerator Driven subcritical System(ADS) is driven by spallation neutrons, which is generated during the proton bombarding the spallation target, to make the subcritical reactor operate stably and continuously. It has high potential to transmute the long-lived minor-actinides and produce cleaner nuclear energy. During the coupling process of the accelerator and reactor, the beam pipeline penetrates through the top cover of the reactor, and spallation neutrons and fission neutrons in the core tend to leak through the pipeline in large quantities. In order to reduce the equipment activation and reduce the personnel radiation dose received during the maintenance, it’s necessary to carry out relevant shielding design work. In the radiation shielding design of thermal spectrum reactor, the thermal neutron fluence rate is usually limited to 105 n/(cm2 · s) to reduce equipment activation and ensure maintainability. For the Accelerator Driven subcritical System, the leakage neutrons from the top cover are fast neutrons with high fluence rate. It is necessary to carry out the shielding design analysis according to an appropriate equivalent thermal neutron fluence rate. This work takes the China initiative Accelerator Driven System(CiADS) as a reference to analyze the expected radiant energy release of activated nuclides generated by the leakage neutrons, and a leakage neutron equivalent fluence rate is obtained. The applicability for this thermal neutron equivalent fluence rate is evaluated. Studies have shown that leakage neutrons with an average fluence rate of 9.292×105 n/(cm2 · s) are equivalent to thermal neutrons with a fluence rate of 105 n/(cm2 · s) in the expected radiant energy release. In the radiation shielding design, the neutron fluence rate limit outside the top cover can be conservatively taken as 8×105 n/(cm2 · s). This research work proposes a method for selecting the equivalent neutron fluence rate in the design of the ADS external activation shield, which can be used in the fast spectrum neutron shielding analysis. The thermal neutron equivalent fluence rate obtained in this paper can provide reference for the shielding design and analysis of CiADS. -
0. 引言
加速器驱动次临界系统(ADS)由加速器、散裂靶、反应堆三个分系统组成,其工作原理是利用强流质子加速器产生高能质子,轰击重金属散裂靶产生宽能谱、高通量的中子,以驱动次临界反应堆持续运行[1]。作为国际公认最有前景的长寿命核废料处理技术,ADS在国内迎来了蓬勃发展。2015年12月,“加速器驱动嬗变研究装置(简称CiADS)” 项目建议书得到了国家发展和改革委员会的批准,CiADS项目正式立项。2018年6月,CiADS的初步设计方案得到了中国科学院的批复。拟于开工6年后,建成世界首台兆瓦级加速器驱动次临界系统[2]。
顶盖屏蔽是反应堆设计过程中不可缺少的环节,也是核电站辐射屏蔽的重要组成部分。它的主要目的是降低堆外设备的活化程度,以允许停堆后检修人员进入维修。然而在“器-靶-堆”结构的ADS装置中,输运质子的真空束流管道贯穿次临界反应堆顶盖,堆芯内的中子极易从真空管道内溢出,会导致管道附近中子注量率上升[3]。CiADS是快中子反应堆,真空束流管道的漏束主要是能谱复杂的快中子,进一步增加了顶盖外辐射屏蔽问题的困难性[4]。为了减小漏束,降低堆外设备被活化的风险,一般有两种常见的解决方案。方案一是在束流管道周围加设屏蔽,然而堆顶在束流管道周围有换靶机构,换料机构等设备,几乎无束管屏蔽所需的空间。即使成功屏蔽,快中子被慢化后产生的热中子,可能会引起更为严重的设备活化;方案二则是优化顶盖设计。通过选取合适的慢化吸收材料并设定适宜的顶盖厚度,达到降低中子注量率的目的。不论何种方案,开展顶盖外辐射屏蔽设计,关键都在于屏蔽设计的目标。热堆中规定顶盖外热中子注量率不超过105 n/(cm2·s),以实现停堆7天后可进人的目的[5]。由于ADS束流管道外是高通量、能谱复杂的快中子,很难限制在105 n/(cm2·s)以下;并且快中子活化能力远低于热中子,采用105 n/(cm2·s)也过于保守。显然,需要建立一套合理可行的等效方案,等效漏束中子与热中子的注量率,以获得适用于ADS的中子注量率标准[6]。
本文基于CiADS堆靶耦合模型,等效ADS顶盖外漏束中子与热中子的预期辐射释能,以获得热中子的等效漏束中子注量率。本文结构如下:第1节介绍等效的原理与方法;第2节是基于CiADS的等效分析;第3节比较不同设计方案与材料选取对等效结果的影响,检测该方法的普适性;第4节是结论与建议。
1. 计算分析方法
1.1 计算方法原理
本文采用等效长寿命放射性核素的预期辐射释能f的方法,以获得快、热中子的等效注量率。预期辐射释能f是长寿命放射性核素的活度A与射线释能D的乘积,单位为MeV,其中,射线释能D为分支比I与对应γ射线能量Eγ的乘积,单位为MeV/Bq,分别如下式所示:
$$ \begin{array}{c}D=I {\boldsymbol{\cdot}} {E}_{\mathrm{\gamma }}, \end{array} $$ (1) $$ \begin{array}{c}f=A{\boldsymbol{\cdot}}I{\boldsymbol{\cdot}}{E}_{\mathrm{\gamma }}=A {\boldsymbol{\cdot}} D。 \end{array} $$ (2) 预期辐射释能f物理意义是放射性核素预期释放的辐射能量,表征的是预期可能造成的辐射损伤的严重程度。
设定反应堆满功率运行三年后停堆,三年后放射性核素的活度A可用下式计算:
$$ \begin{array}{c}A=s\left(1-{\rm e}^{-\lambda t}\right), \end{array} $$ (3) 其中:A为时间t时刻的核素活度;s为核素每秒的产生量,即产生率;
$ \lambda $ 为核素衰变常数。其中,产生率s:$$ s=\phi {\boldsymbol{\cdot}} \sigma {\boldsymbol{\cdot}} N {\boldsymbol{\cdot}} V , $$ (4) 其中:
$\phi $ 为中子注量率;$ \sigma $ 为中子微观反应截面;N为核素原子密度;V表示体积。将式(4)带入式(3)中即可得:$$ A=s\left(1-{\rm e}^{-\lambda t}\right)=\phi {\boldsymbol{\cdot}} \sigma {\boldsymbol{\cdot}} N {\boldsymbol{\cdot}} V\left(1-{\rm e}^{-\lambda t}\right) , $$ (5) $$ f=\phi {\boldsymbol{\cdot}} \sigma {\boldsymbol{\cdot}} N {\boldsymbol{\cdot}} V\left(1-{\rm e}^{-{\lambda}t}\right) {\boldsymbol{\cdot}} D ,$$ (6) 根据式(6),即可算得放射性核素的预期辐射释能f。然而,并非所有放射性核素都会对维修人员造成辐射损伤。在停堆的七天内,半衰期较短的放射性核素会快速衰变,如式(7)所示:
$$ \begin{array}{c}N={N}_{0} {\boldsymbol{ \cdot}} {\rm e}^{-{\lambda}t} \end{array} , $$ (7) 式中:N为时间t时的核素原子数目;N0为核素初始原子数目;
$ \lambda $ 为衰变常数。由该公式可得,当核素半衰期为86 400 s(24 h)时,衰变7 d后的剩余核仅为0.782%,可忽略不计。在本文中,半衰期低于86 400 s的放射性核素将被忽略。此外,由于α、β射线电离能力强而穿透力弱,一张薄纸、一块砖便可轻易阻挡[7],对维修人员造成的辐射损伤可忽略不计,在等效过程中也将被忽略。最后,由于X射线相对$ \gamma $ 射线能量较低,穿透力较弱,因而本文将$ \gamma $ 射线视作辐照损伤的主要原因,着重研究释放$ \gamma $ 射线的长寿命放射性核素。由快、热中子活化得到的长寿命放射性核素衰变时释放的
$ \gamma $ 射线的总预期辐射释能,分别由${F}_{\mathrm{\gamma }\mathrm{f}}$ 与${F}_{\mathrm{\gamma }\mathrm{th}}$ 表示,可由式(8)、式(9)计算:$$ F_{\gamma \mathrm{f}}=\phi_{\mathrm{f}} {\boldsymbol{\cdot}} V \sum_i \sigma_i {\boldsymbol{\cdot}} N_i {\boldsymbol{\cdot}} D_i\left(1-{\rm e}^{-\lambda_i t}\right), $$ (8) $$F_{\gamma \mathrm{th}}=\phi_{\mathrm{th}} {\boldsymbol{\cdot}} V \sum_j \sigma_j {\boldsymbol{\cdot }}N_j {\boldsymbol{\cdot}} D_j\left(1-{\rm e}^{-\lambda_j t}\right)。 $$ (9) 当快、热中子预期辐射释能相等,即
${F}_{\mathrm{\gamma }\mathrm{f}}={F}_{\mathrm{\gamma }\mathrm{th}}$ 时,可用式(10)计算漏束中子的等效注量率$ {\phi}_{\mathrm{f}} $ :$$ \phi_{\mathrm{f}}=\frac{\phi_{\mathrm{th}} \sum_j \sigma_j{\boldsymbol{ \cdot}} N_j {\boldsymbol{\cdot }}D_j\left(1-{\rm e}^{-\lambda_j t}\right)}{\sum_i \sigma_i {\boldsymbol{\cdot }}N_i {\boldsymbol{\cdot}} D_i\left(1-{\rm e}^{-\lambda_i \mathrm{t}}\right)},$$ (10) 其中:设定
$\sigma \cdot N \cdot D\left(1-{\rm e}^{-\lambda t}\right)$ 为等效释能宏观截面,用k表示,如式(11)所示;总等效释能宏观截面K如式(12)所示:$$ \begin{array}{c}k=\sigma {\boldsymbol{\cdot}}N {\boldsymbol{\cdot}} D\left(1-{\rm e}^{-\lambda t}\right), \end{array} $$ (11) $$ {K}_{i}=\sum _{i}{\sigma }_{i} {\boldsymbol{\cdot}}{N}_{i} {\boldsymbol{\cdot}}{D}_{i}\left(1-{\rm e}^{-{\lambda }_{i}t}\right), $$ (12) 则式(10)可简化为
$$ {\phi}_{\mathrm{f}}=\frac{{\phi}_{\mathrm{th}} {\boldsymbol{\cdot}}{K}_{j}}{{K}_{i}}。 $$ (13) 1.2 数据获取方法
为了统计被热中子活化产生的长放射性核素,建立一个厚度0.1 cm以及半径200 cm的圆台,如图1所示,并在周围填充空气。在圆台下方设置6个均匀分布的强平行热中子源击打圆台,令圆台被充分活化,以获得活化后的放射性核素种类。而热中子反应截面,可通过查询ENDF数据库直接获取。
但对于快中子而言,由于真空束流管道外快中子能谱复杂,无法查询数据获取。因此可向栅元内填充虚拟材料,统计该栅元内的中子通量以及反应率,利用式(14)计算微观截面σ:
$$ R=\phi {\boldsymbol{\cdot}} N {\boldsymbol{\cdot}} \sigma,$$ (14) 其中:R为反应率;
$\phi $ 为中子注量率;N为核素原子密度;$\sigma $ 为微观反应截面。射线释能D可通过查询NuDat3直接获取。
2. 基于CiADS模型的评估
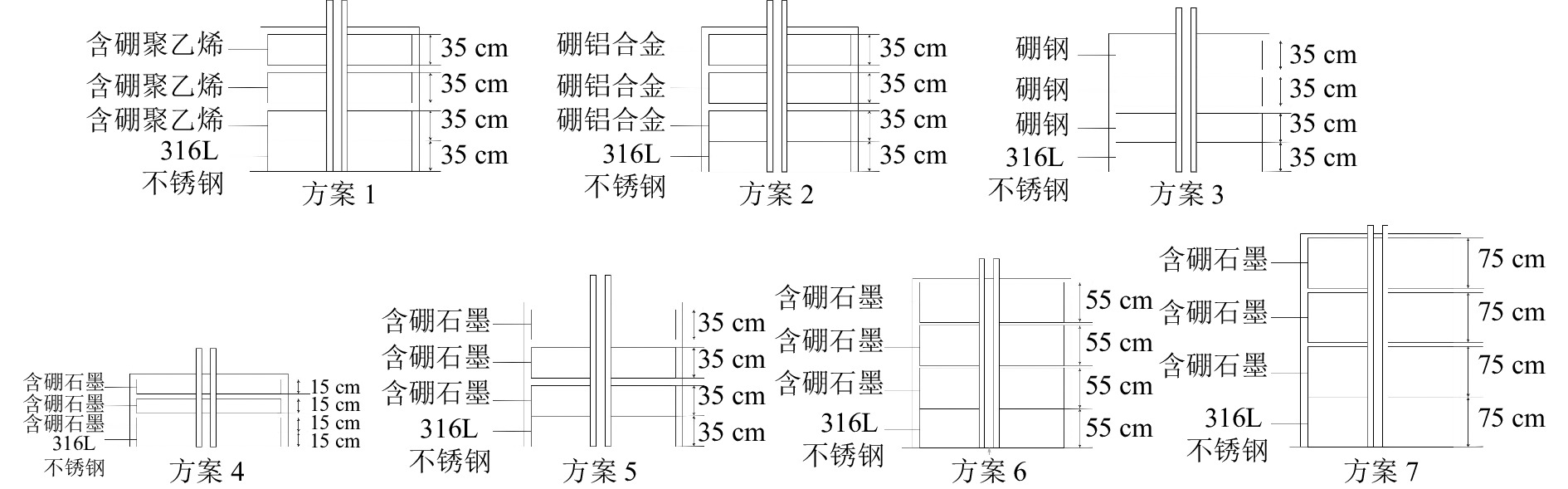
本文以CiADS为模型研究漏束中子与热中子的等效注量率。设定CiADS顶盖为316L不锈钢盒模型,内部分四层,最底层采用与不锈钢盒同种的316L不锈钢填充[4],另外三层填充含硼聚乙烯。填充材料的厚度均为35 cm。整个顶盖被真空束流管道贯穿,简化模型如图2所示。在本文中,主要研究顶盖外束流管道内最外侧316L不锈钢的活化情况,即图2中的栅元83。栅元83内不锈钢的活化最接近顶盖外部设备的活化情况。
使用蒙特卡罗程序从CiADS模型中读取顶盖出口处的快中子能谱,将其作为简化后CiADS模型的中子源进行模拟计算,快中子能量分布如图3所示。经统计,栅元83内残留的衰变时释放
$ \gamma $ 射线的长放射性核素种类及其部分参数如表1所列。表 1 栅元83内残留放射性核素统计长放射性核素 衰变常数λ/s−1 产生率s/n·s−1 3年累积核素活度A/Bq 射线释能Dose[8]
/MeV·Bq−1预期辐射释能f/MeV 预期辐射释能f占比/% 50V 1.575 3×10−25 4.624 3×10−10 0.000 000×100 1.543×100 0.000 000×100 0.000 51Cr 2.896 0×10−7 5.632 7×10−9 1.760 219×108 3.200×10−2 5.583 414×106 1.201 54Mn 2.570 4×10−8 4.179 8×10−9 1.191 403×108 0.835×100 9.944 018×107 21.388 55Fe 8.030 9×10−9 1.265 4×10−8 2.104 719×108 1.610×10−10 3.388 598×10−2 0.000 59Fe 1.803 0×10−7 4.624 4×10−10 1.445 137×107 1.188×100 1.717 143×107 3.693 57Co 2.952 3×10−8 2.111 1×10−11 6.193 190×105 0.122×100 7.528 658×104 0.016 58Co 1.132 2×10−7 1.199 7×10−8 3.749 041×108 0.821×100 3.077 551×108 66.192 60Co 4.166 8×10−9 1.238 1×10−10 1.260 509×106 2.504×100 3.156 156×106 0.679 57Ni 5.415 2×10−6 2.591 1×10−11 8.097 156×105 1.497×100 1.211 755×106 0.261 89Zr 2.455 4×10−6 5.055 9×10−12 1.579 959×105 0.918×100 1.450 798×105 0.031 93Zr 1.435 1×10−14 6.294 1×10−13 2.670 480×10−2 1.330×10−7 3.551 738×10−9 0.000 95Zr 1.252 9×10−7 3.157 8×10−13 9.867 961×103 0.733×100 7.230 650×103 0.002 92Nb 6.301 3×10−16 3.893 1×10−11 7.252 804×10−2 1.250×100 9.066 005×10−2 0.000 94Nb 1.081 4×10−12 1.984 1×10−12 6.342 782×100 1.572×100 9.967 689×100 0.000 95Nb 2.292 8×10−7 8.912 2×10−13 2.785 066×104 0.764×100 2.129 102×104 0.005 93Mo 5.331 9×10−12 1.707 4×10−9 2.690 872×104 1.600×10−7 4.305 396×10−3 0.000 99Mo 2.919 7×10−6 6.824 5×10−9 2.132 663×108 0.142×100 3.037 613×107 6.533 由表1可得,54Mn、59Fe、58Co、99Mo四种核素,贡献了主要的预期辐射释能,其占比都在3%以上。然而,99Mo的半衰期为2.748 d,根据式(6),在停堆7 d后,其原子数目将衰变至17.47%,占比大大减少。因此可认为54Mn、59Fe以及58Co贡献了主要的预期辐射释能。
生成这三种核素的中子反应,是CiADS堆外设备被活化后对外造成辐射损伤的主要原因。通过向栅元83内部填充虚拟材料,可获得该栅元内中子反应的反应率,结合中子注量率,可算得平均反应截面,如表2所列。获得平均微观反应截面后,即可计算等效释能宏观截面,如表3所列。
表 2 束流管道外漏束中子的平均微观反应截面中子反应类型 中子通量φ/(n·cm−2·source particle−1) 反应率R/(n·cm−3·source particle−1) 平均微观反应截面σ/b 54Fe(n,p)54Mn 1.435 1×10−8 8.238 0×10−11 5.740 6×10−3 55Mn(n,2n)54Mn 1.435 1×10−8 5.734 5×10−12 3.996 0×10−4 58Fe(n,γ)59Fe 1.435 1×10−8 2.194 3×10−10 1.529 1×10−2 58Ni(n,p)58Co 1.435 1×10−8 1.253 0×10−10 8.731 4×10−3 表 3 束流管道外漏束中子的等效释能宏观截面长放射性核素 Dose[8]/
(MeV·Bq-s-1)原核素原子密度N/
(n·cm-3)(1-e−λt) 平均微观
反应截面σ/b等效释能
宏观截面k总等效释能
宏观截面K54Mn 0.835 3.289 2×10−3 9.121 18×10−1 5.740 6×10−3 1.437 5×10−5 6.573 0×10−5 54Mn 0.835 1.749 5×10−3 9.121 18×10−1 3.996 0×10−4 5.322 2×10−7 59Fe 1.188 1.586 9×10−4 1.000 00×100 1.529 1×10−2 2.883 2×10−6 58Co 0.821 6.688 7×10−3 9.999 78×10−1 8.731 4×10−3 4.794 0×10−5 同理,对热中子进行等效处理。热中子模型同样采用316L不锈钢材作为活化材料,热中子仅发生(n,
$\lambda $ )反应,反应截面可通过查询获取,其结果如表4所列。将上述数据带入式式(9),取
$ {\phi}_{\mathrm{t}\mathrm{h}} $ =105 n/(cm2·s),可得在预期辐射释能相等的条件下,105 n/(cm2·s)的热中子注量率近似等效于CiADS束流管道外8.847×105 n/(cm2·s)的漏束中子注量率。3. 适用性评估
在实际应用中,当顶盖的厚度、材料选择不同时,CiADS的漏束中子能谱、漏束中子反应截面也不尽相同。为了验证该方法的普适性,本文通过分别更改所选材料的种类以及厚度,探究漏束中子、热中子等效注量率与顶盖结构的关系,如图4所示。七种顶盖结构设计方案分别为:底层填充厚度为35 cm的316L不锈钢,另外三层填充厚度为35 cm的含硼聚乙烯;底层填充厚度为35 cm的316L不锈钢,另外三层填充厚度为35 cm的硼铝合金;底层填充厚度为35 cm的316L不锈钢,另外三层填充厚度为35 cm的硼钢;底层填充厚度为35 cm的316L不锈钢,另外三层填充厚度为35 cm的含硼石墨;底层填充厚度为15 cm的316L不锈钢,另外三层填充厚度为15 cm的含硼石墨;底层填充厚度为55 cm的316L不锈钢,另外三层填充厚度为55 cm的含硼石墨;底层填充厚度为75 cm的316L不锈钢,另外三层填充厚度为75 cm的含硼石墨。
此外,虽然ADS中主要应用316L不锈钢,但在热堆中,304不锈钢、316不锈钢同样广泛使用[10]。因此本文也将针对不同的不锈钢材,计算热中子的总等效释能宏观截面,探究不锈钢材种类对等效注量率的影响。
对于不同的顶盖结构,其漏束中子的等效释能宏观截面如表5所列。
表 5 不同顶盖结构下漏束中子的总等效释能宏观截面顶盖结构 方案一 方案二 方案三 方案四 方案五 方案六 方案七 总等效释能
宏观截面K6.573×10−5 6.279×10−5 6.155×10−5 6.123×10−5 6.311×10−5 6.267×10−5 6.368×10−5 对于不同的不锈钢材,热中子的等效释能宏观截面如表6所列。
表 6 不同活化钢材下热中子的总等效释能宏观截面不锈钢材种类 316 304 316L 总等效释能宏观截面K 5.872 2×10−4 6.388 6×10−4 5.815 1×10−4 将上述数据带入式(9),取
$ {\phi}_{\mathrm{t}\mathrm{h}} $ =105 n/(cm2·s),可得当预期辐射释能相等时,不同条件下漏束中子的等效注量率。计算结果与平均值如表7所列,其与总平均值的偏差如表8所列。表 7 不同条件下的等效漏束中子注量率
方案等效注量率$\phi_{\rm f}$
/(n·cm-2·s-1)平均等效
注量率$\overline{\phi_{\rm f}}$
/(n·cm−2·s−1)热中子活化材料为316L 热中子活化材料为316 热中子活化材料为304 方案一 8.847×105 8.934×105 8.949×105 8.910×105 方案二 9.261×105 9.352×105 9.380×105 9.331×105 方案三 9.448×105 9.541×105 9.515×105 9.501×105 方案四 9.497×105 9.590×105 9.444×105 9.511×105 方案五 9.215×105 9.305×105 9.271×105 9.264×105 方案六 9.279×105 9.370×105 9.327×105 9.325×105 方案七 9.131×105 9.221×105 9.250×105 9.201×105 平均等效注量率$\overline{\phi_{\rm f}}$
/(n·cm−2·s−1)9.240×105 9.330×105 9.305×105 9.292×105 表 8 不同情况下的等效漏束中子注量率与总平均值的偏差方案 偏差/% 热中子活化
材料为316L热中子活化
材料为316热中子活化
材料为304方案一 −4.787 −3.852 −3.692 方案二 −0.331 0.647 0.946 方案三 1.681 2.679 2.403 方案四 2.209 3.212 1.644 方案五 −0.828 0.145 −0.221 方案六 −0.139 0.841 0.382 方案七 −1.725 −0.761 −0.452 由表7和8可以看出,在基于预期辐射释能的等效下,顶盖材料与厚度、中子活化材料的改变,对等效注量率有一定影响,导致所获得的等效注量率存在5%以内的偏差。但该偏差较小,可以忽略。这证明了以基于等效预期辐射释能的方法获得的热中子与漏束中子等效注量率,受顶盖设计与材料变化的影响较小,具有一定的普适性。
基于预期辐射释能的等效,算得105 n/(cm2·s)的热中子的平均等效漏束中子注量率约为9.292×105 n/(cm2·s)。在常见的三种不锈钢材料中,316L相对较难活化,其等效结果也最为保守,具有较高的参考意义。在实际应用中,ADS内可保守限制中子注量率至8×105 n/(cm2·s)。
4. 结论
本文面向ADS的束流漏束分析,开展了热中子等效中子注量率的计算与评估。采用了以等效预期辐射释能的方法,使用CiADS为研究模型展开了分析与计算。随后通过比较不同顶盖结构的影响与中子活化材料更变的影响,验证了该方法的适用性。结果表明,注量率为9.292×105 n/(cm2·s)的漏束中子在辐射释能上等效于105 n/(cm2·s)的热中子。受不同顶盖设计与活化材料的影响,存在上下5%的偏差。虽然快热谱下材料俘获截面相差两个量级以上,但由于高能中子与材料存在(n, p)、(n, 2n)等反应,CiADS漏束中子与热中子等效注量率仅相差8~10倍。在ADS内辐射屏蔽相关设计中,可保守认为8×105 n/(cm2·s)为顶盖外漏束中子注量率限值。研究工作提出了一种ADS堆外活化屏蔽设计时的热中子等效注量率的选取方法,可为快谱下的屏蔽分析提供参考。本文获得的热中子等效注量率可用于CiADS顶盖屏蔽的工程设计与分析。
-
表 1 栅元83内残留放射性核素统计
长放射性核素 衰变常数λ/s−1 产生率s/n·s−1 3年累积核素活度A/Bq 射线释能Dose[8]
/MeV·Bq−1预期辐射释能f/MeV 预期辐射释能f占比/% 50V 1.575 3×10−25 4.624 3×10−10 0.000 000×100 1.543×100 0.000 000×100 0.000 51Cr 2.896 0×10−7 5.632 7×10−9 1.760 219×108 3.200×10−2 5.583 414×106 1.201 54Mn 2.570 4×10−8 4.179 8×10−9 1.191 403×108 0.835×100 9.944 018×107 21.388 55Fe 8.030 9×10−9 1.265 4×10−8 2.104 719×108 1.610×10−10 3.388 598×10−2 0.000 59Fe 1.803 0×10−7 4.624 4×10−10 1.445 137×107 1.188×100 1.717 143×107 3.693 57Co 2.952 3×10−8 2.111 1×10−11 6.193 190×105 0.122×100 7.528 658×104 0.016 58Co 1.132 2×10−7 1.199 7×10−8 3.749 041×108 0.821×100 3.077 551×108 66.192 60Co 4.166 8×10−9 1.238 1×10−10 1.260 509×106 2.504×100 3.156 156×106 0.679 57Ni 5.415 2×10−6 2.591 1×10−11 8.097 156×105 1.497×100 1.211 755×106 0.261 89Zr 2.455 4×10−6 5.055 9×10−12 1.579 959×105 0.918×100 1.450 798×105 0.031 93Zr 1.435 1×10−14 6.294 1×10−13 2.670 480×10−2 1.330×10−7 3.551 738×10−9 0.000 95Zr 1.252 9×10−7 3.157 8×10−13 9.867 961×103 0.733×100 7.230 650×103 0.002 92Nb 6.301 3×10−16 3.893 1×10−11 7.252 804×10−2 1.250×100 9.066 005×10−2 0.000 94Nb 1.081 4×10−12 1.984 1×10−12 6.342 782×100 1.572×100 9.967 689×100 0.000 95Nb 2.292 8×10−7 8.912 2×10−13 2.785 066×104 0.764×100 2.129 102×104 0.005 93Mo 5.331 9×10−12 1.707 4×10−9 2.690 872×104 1.600×10−7 4.305 396×10−3 0.000 99Mo 2.919 7×10−6 6.824 5×10−9 2.132 663×108 0.142×100 3.037 613×107 6.533 表 2 束流管道外漏束中子的平均微观反应截面
中子反应类型 中子通量φ/(n·cm−2·source particle−1) 反应率R/(n·cm−3·source particle−1) 平均微观反应截面σ/b 54Fe(n,p)54Mn 1.435 1×10−8 8.238 0×10−11 5.740 6×10−3 55Mn(n,2n)54Mn 1.435 1×10−8 5.734 5×10−12 3.996 0×10−4 58Fe(n,γ)59Fe 1.435 1×10−8 2.194 3×10−10 1.529 1×10−2 58Ni(n,p)58Co 1.435 1×10−8 1.253 0×10−10 8.731 4×10−3 表 3 束流管道外漏束中子的等效释能宏观截面
长放射性核素 Dose[8]/
(MeV·Bq-s-1)原核素原子密度N/
(n·cm-3)(1-e−λt) 平均微观
反应截面σ/b等效释能
宏观截面k总等效释能
宏观截面K54Mn 0.835 3.289 2×10−3 9.121 18×10−1 5.740 6×10−3 1.437 5×10−5 6.573 0×10−5 54Mn 0.835 1.749 5×10−3 9.121 18×10−1 3.996 0×10−4 5.322 2×10−7 59Fe 1.188 1.586 9×10−4 1.000 00×100 1.529 1×10−2 2.883 2×10−6 58Co 0.821 6.688 7×10−3 9.999 78×10−1 8.731 4×10−3 4.794 0×10−5 表 4 热中子的等效处理
表 5 不同顶盖结构下漏束中子的总等效释能宏观截面
顶盖结构 方案一 方案二 方案三 方案四 方案五 方案六 方案七 总等效释能
宏观截面K6.573×10−5 6.279×10−5 6.155×10−5 6.123×10−5 6.311×10−5 6.267×10−5 6.368×10−5 表 6 不同活化钢材下热中子的总等效释能宏观截面
不锈钢材种类 316 304 316L 总等效释能宏观截面K 5.872 2×10−4 6.388 6×10−4 5.815 1×10−4 表 7 不同条件下的等效漏束中子注量率
方案等效注量率$\phi_{\rm f}$
/(n·cm-2·s-1)平均等效
注量率$\overline{\phi_{\rm f}}$
/(n·cm−2·s−1)热中子活化材料为316L 热中子活化材料为316 热中子活化材料为304 方案一 8.847×105 8.934×105 8.949×105 8.910×105 方案二 9.261×105 9.352×105 9.380×105 9.331×105 方案三 9.448×105 9.541×105 9.515×105 9.501×105 方案四 9.497×105 9.590×105 9.444×105 9.511×105 方案五 9.215×105 9.305×105 9.271×105 9.264×105 方案六 9.279×105 9.370×105 9.327×105 9.325×105 方案七 9.131×105 9.221×105 9.250×105 9.201×105 平均等效注量率$\overline{\phi_{\rm f}}$
/(n·cm−2·s−1)9.240×105 9.330×105 9.305×105 9.292×105 表 8 不同情况下的等效漏束中子注量率与总平均值的偏差
方案 偏差/% 热中子活化
材料为316L热中子活化
材料为316热中子活化
材料为304方案一 −4.787 −3.852 −3.692 方案二 −0.331 0.647 0.946 方案三 1.681 2.679 2.403 方案四 2.209 3.212 1.644 方案五 −0.828 0.145 −0.221 方案六 −0.139 0.841 0.382 方案七 −1.725 −0.761 −0.452 -
[1] (肖国青, 徐瑚珊, 王思成. 原子核物理评论, 2017, 34(03): 275. DOI: 10.11804/NuclPhysRev.34.03.275 XIAO Guoqing, XU Hushan, WANG Sicheng. Nuclear Physics Review, 2017, 34(03): 275. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11804/NuclPhysRev.34.03.275
[2] 张宏韬, 席斌, 顾龙, 等. 基于加速器驱动嬗变研究装置(CiADS)的铅基快堆关键技术研发与挑战[C]//中国核科学技术进展报告(第六卷)——中国核学会2019年学术年会论文集第3册(核能动力分卷). 北京: 中国原子能出版社, 2019: 320. ZHANG Hongtao, XI Bin, GU Long, et al. R&D and Challenges of Key Technologies for Lead-Based Fast Reactors Based on Accelerator-Driven Transmutation Research Device (CiADS)[C]//Progress Report on China's Nuclear Science and Technology (Volume 6)-Proceedings of the 2019 Annual Conference of the China Nuclear Society, Volume 3 (Volume on Nuclear Power). Beijing: China Atomic Press, 2019: 320. (in Chinese)
[3] LI Bin, YANG Qi, CHANG Bo, et al. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2016, 90: 410. DOI: 10.1016/j.anucene.2015.12.012
[4] 李斌. 加速器驱动次临界系统堆顶辐射特征研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2016. LI Bin. Research on the Radiation Characteristics of the Top of the Accelerator Driven Subcritical System[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2016. (in Chinese)
[5] 李长园. 铝基碳化硼复合材料中子屏蔽性能研究[D]. 上海: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院上海应用物理研究所), 2021. LI Changyuan. Research on Neutron Shielding Properties of Aluminum-based Boron Carbide Composites[D]. Shanghai: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2021. (in Chinese)
[6] 钠冷快中子增殖堆设计准则屏蔽设计: EJ/T20104-2016[S]. 北京: 核工业标准化研究所, 2016. State Administration of Science. Design Criteria for Sodium Cooled Fast Breeder Reactor Shield Design: EJ/T20104-2016[S]. Beijing: Nuclear Industry Standardization Research Institute, 2016. (in Chinese)
[7] 马新安, 陈功, 张莹, 等. 服装学报, 2019, 4(02): 95. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7147.2019.02.001 MA Xin'an, CHEN Gong, ZHANG Ying, et al. Journal of Clothing, 2019, 4(02): 95. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7147.2019.02.001
[8] NuDat3[EB/OL]. [2022-08-15]. https://www.nndc.bnl.gov/nudat3/.
[9] ENDF[EB/OL]. [2022-08-15]. https://www.nndc.bnl.gov/endf/.
[10] KUMAR P, SONI R K, DEHIYA B S, et al. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2021, 47(19): 6545. DOI: 10.1016/j.matpr.2021.01.815




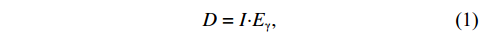
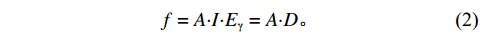
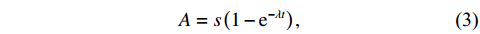
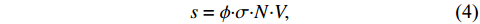
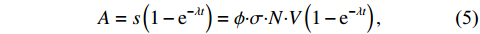
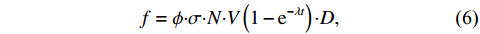
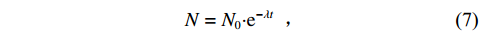
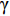
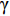
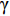
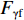
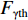
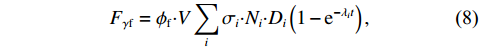
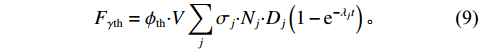
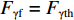
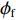
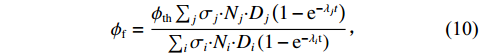
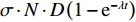
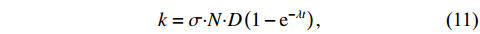
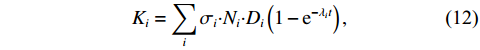
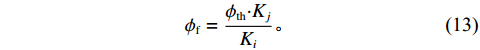

 下载:
下载:
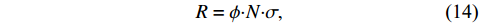
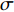

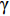

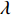
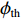
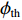
 甘公网安备 62010202000723号
甘公网安备 62010202000723号