Ion Implantation/Irradiation System of 1.7 MV Tandem Accelerator at Peking University
-
摘要: 北京大学1.7 MV串列静电加速器运行至今已有三十多年。该加速器配备有高频电荷交换负离子源和铯溅射负离子源,能够引出从H到 Au之间 的大部分元素的离子。离子能量可被加速至几百keV到若干MeV,主要开展离子注入/辐照实验和卢瑟福背散射(RBS)和沟道分析等离子束分析工作。基于辐照实验需求,建立了高温辐照系统,温度最高可达950 ℃。为了实现更加精确的离子注入,设计了直接式与间接式两种法拉第杯结构,使束流扫描面积精确控制,并且在测量束流强度时除了抑制次级电子,还考虑到了次级正离子的影响。利用不同能量的Au离子在单晶Si片上进行了注入实验,通过RBS分析显示测量剂量与期望剂量误差在4%以内,此外,注入均匀性的测试表明注入剂量的相对标准偏差为2%。Abstract: The 1.7 MV tandem accelerator at Peking University has been running for more than 30 years. The accelerator is equipped with a Radio Frequency(RF) charge exchange negative ion source and a cesium sputtering negative ion source, which can produce most of the ions from H to Au. It can accelerate the ions to energies from several hundreds of keV to several MeV. The accelerator is used for ion implantation and irradiation as well as for ion beam analysis, such as Rutherford Backscattering Spectroscopy(RBS) and channeling. Based on the experimental requirements, a high temperature irradiation system was established, with the highest temperature of 950 ℃. In order to achieve more accurate ion implantation, two Faraday cup structures, direct type and indirect type, are designed. The scanning area of the beam is controlled accurately. These designs can not only suppress the secondary electrons, the influence of secondary positive ions is also considered when measuring the beam intensity. The ion implantation experiments of Au ions with different energy on single crystal silicon were carried out. RBS analysis shows that the error between the measured fluence and the expected fluence is within 4%. In addition, the uniformity measurement shows that the relative standard deviation of the implant fluence is 2%.
-
1. 引言
载能离子进入材料中后,主要以核能损和电子能损的方式将能量传递给靶原子,使它们激发、电离或移位,从而在材料中造成一定的损伤,产生缺陷;载能离子在损失了动能后,最后将停留在靶中,这就是离子的掺杂效应。通常人们将掺杂离子的过程称为离子注入,而将其对材料的损伤效应称为离子辐照。离子束在材料科学,特别是在先进能源材料研究等领域具有广阔的应用前景。对于先进核能系统,核能反应堆中的大量结构材料在高能中子辐照条件下,会产生结构损伤和性能退化。因此,材料的抗辐照性能是影响核反应堆运行安全的重要因素之一。离子辐照不仅能产生与反应堆中子辐照相类似的原子离位损伤,而且相对于中子辐照具有实验周期短、成本低及辐照后样品无放射性等优点,因此大多数核能材料辐照损伤的研究及新型抗辐照材料的初步筛选,都是通过离子辐照来模拟研究中子对材料的辐照损伤。近年,北京大学核技术应用实验室和国内外合作团队利用北京大学的1.7 MV串列静电加速器等加速器设备引出的重离子系统研究了纳米多层膜、金属/陶瓷界面、金属玻璃、纳米晶钨基材料、纳米多孔材料、高熵合金和多种铁基合金材料的辐照效应,在原子尺度上揭示了这些材料的辐照损伤机制 [ 1- 10] 。同时,利用低、高能离子改性材料,显著提高了多种电化学催化材料、功能薄膜材料和纳米发电材料等清洁能源材料的各种性能 [ 11- 15] 。
本文将对北京大学1.7 MV串列静电加速器的离子注入/辐照实验系统进行介绍。离子注入/辐照剂量的大小与掺杂物质的含量、材料辐照损伤的程度等直接相关,因此其准确性十分重要,需要经常进行剂量校准。在前期校准实验中我们发现,注入/辐照剂量的测量值与期望值最大误差可达10%以上。为了提高离子注入/辐照剂量的准确度,本文设计了直接式与间接式两种法拉第杯结构,应用于MeV量级离子注入实验时,测量剂量与期望剂量误差在4%以内。
2. 装置简介
北京大学1.7 MV串列静电加速器由20世纪80年代从美国国家静电公司(National Electrostatics Corp., NEC)进口,型号为5SDH-2,运行至今已有三十多年。该加速器配备有高频电荷交换负离子源和铯溅射负离子源,可引出从H到Au之间的大部分元素的离子。其端电压从240 kV~1.7 MV 连续可调,可将离子源引出的离子加速至几百keV到若干MeV,束流强度从nA到μA量级(不同离子的束流强度会有差别)。目前建有三条束流线, 主要开展室温和高温的离子注入/辐照实验和卢瑟福背散射(RBS)和沟道分析等离子束分析工作。作为北京大学核物理与核技术国家重点实验室和北京大学核技术应用实验室(Ion Beam Materials Laboratory, IBML)的大型仪器设备之一,每年承担多项开放课题项目,提高了设备的利用效率。近五年来已为校外40多家高校和科研院所的50余个课题组提供高质量束流服务和实验测试服务,取得了较好的科研成果和社会效益,对我国核能材料发展和离子束材料改性研究做出了重要的贡献。
2.1 离子注入/辐照束线介绍
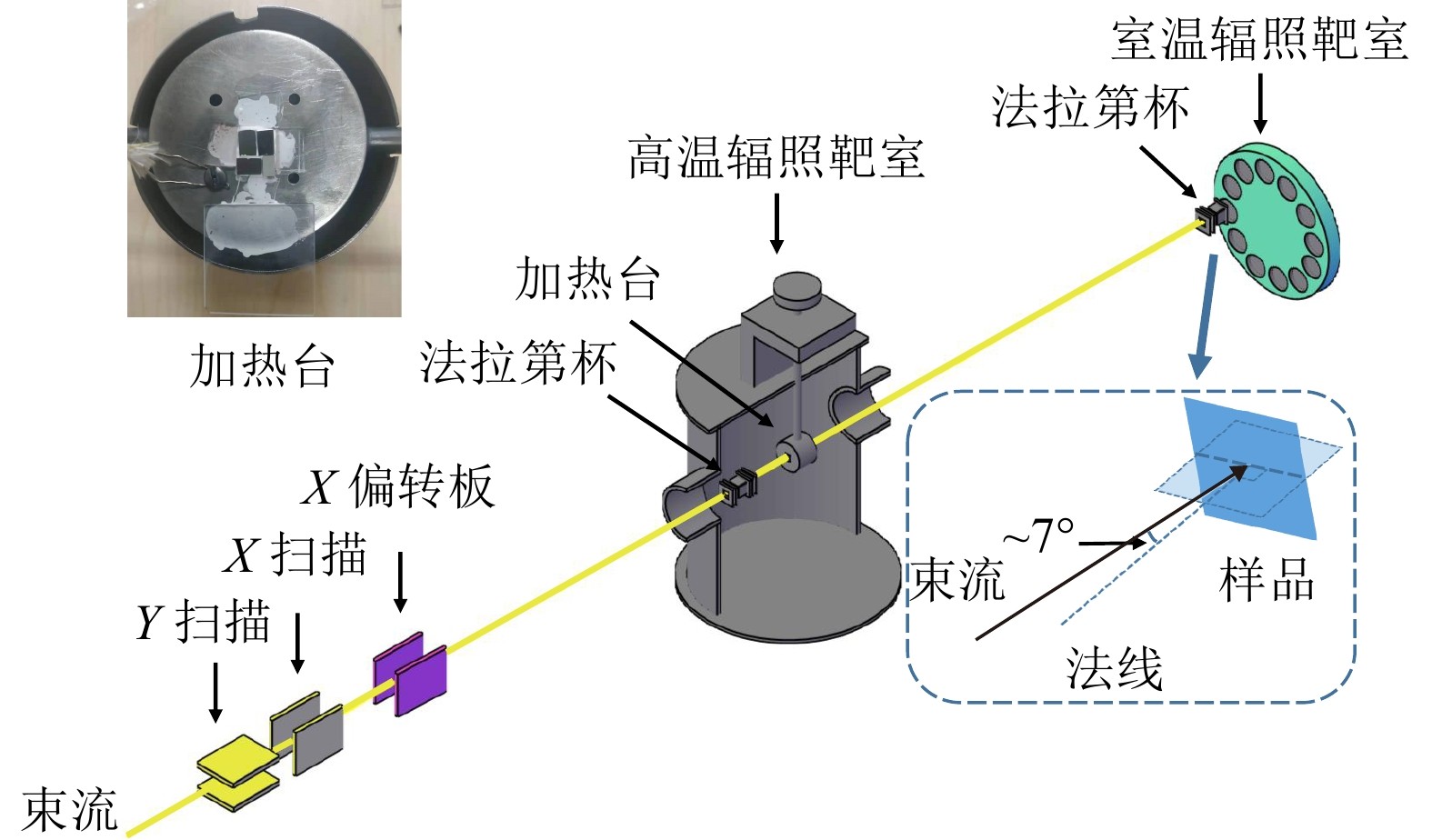
离子注入/辐照束线主要结构如 图1所示。选定能量的离子束通过磁分析器后经过扫描器在垂直( Y)和水平( X)两个方向进行扫描,再经过 X方向偏转装置将离子束偏转一定角度打到样品上。扫描器是由中国电子科技集团公司第四十八研究所(长沙48所)制造,扫描电源购自NEC公司, X方向快扫频率517 Hz, Y方向慢扫频率64 Hz。注入束线上有高温和室温辐照两个靶室。后面的室温靶室较小,其旋转靶盘上有12个圆槽,直径40 mm,其中一个槽中装有石英片,在后置观察窗中可以观察扫描前后束斑位置及大小,其余圆槽可放入铜片。铜片上的样品需用导电胶粘牢,样品范围不超过20 mm×20 mm,一次可放多组样品,依次进行不同注入剂量的辐照实验。靶室内装有法拉第杯,杯底即靶盘。样品表面与靶盘表面夹角6°,离子束偏转装置使束流与靶盘偏约1°,因此束流与样品表面法线夹角约7°,以避免注入时的沟道效应。在离子注入过程中, 注入离子淀积的能量以热的形式消耗,将使样品温度升高。为此,在不加热的情况下,利用热电偶测试了温度上升情况。测试束流为3 MeV的Au 2+,流强约1 μA,扫描面积14 mm×14 mm,剂量率约为1.6×10 12 cm –2 s –1,1.5 h后,温度接近70 ℃。对于室温辐照实验,剂量率一般处于1.0×10 11 cm –2 s –1至1.5×10 12 cm –2 s –1之间,因此样品的温升不会很高。
由于先进核能系统反应堆的运行环境多为高温、强辐照,因此为了满足对高温辐照实验的需求,在前面大靶室建立了高温辐照系统。高温辐照系统主要由加热台、温控装置、测温部分和法拉第杯构成。加热台通过电流加热,其直径约50 mm,上面有四个螺孔,可固定热电偶或夹片。为了提高传热效率,样品可用高温胶固定,样品范围一般不超过10 mm×10 mm。温控装置通过加热台上端热电偶反馈的温度控制输出电流的大小,使加热台温度稳定在设置值,加热温度一般在100~950 ℃之间。样品温度由加热台左侧的热电偶测量。流强的测量是通过加热台前方的法拉第杯。
2.2 离子注入/辐照实验要求和设计
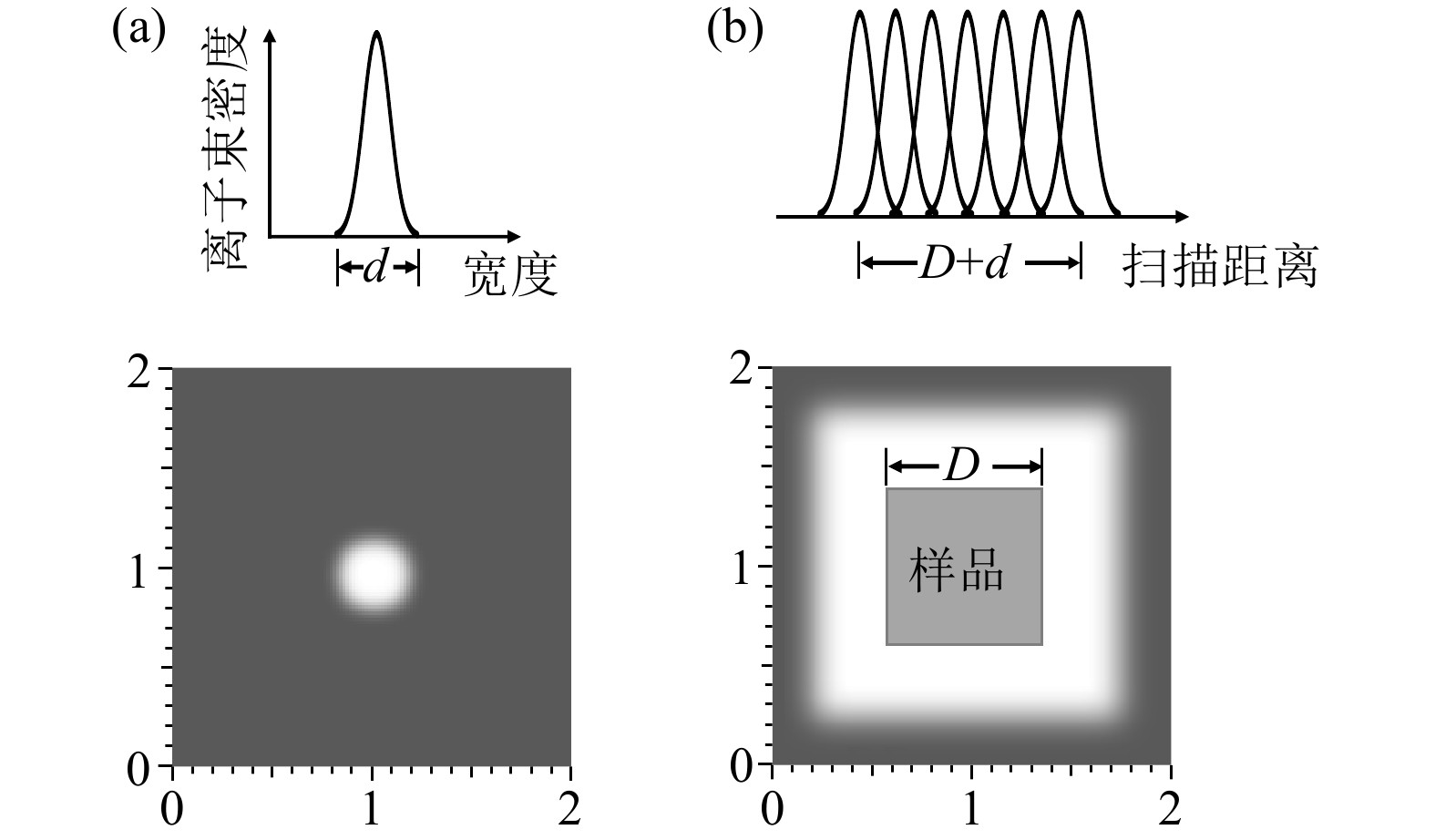
在离子注入实验中,对样品的均匀注入是基本的技术要求。显然,利用直径为几mm的离子束,固定注入样品的某部位是不行的。首先,离子束横截面的束流密度分布是不均匀的;其次,离子束能量集中于样品表面局部可能会引起样品表面温度太高。为了保证对样品实现均匀注入,通常采用静电扫描、机械扫描或混合扫描等扫描方式。本设备束线采用了静电扫描的方式。为了提高注入的均匀性,除了采用离子束偏转装置以避开中性束,还需要对样品进行过扫描。如 图2所示,设离子束横截面的束流密度分布近似是高斯分布,束斑尺寸为 d,样品尺寸为 D,则扫描幅度至少要达到 D+ d,才能保证束流打在样品上的部分是均匀的。显然,单方向扫描的束流有效利用率为(1– d/ D),双向扫描的利用率为(1– d/ D) 2。为了保证注入剂量的准确度和精确度,束流强度和注入面积的确定将十分重要。在离子注入过程中,若束流强度稳定为 I,则Δ t时间内积累的电荷量为 IΔ t,当扫描面积为 S时,对应的注入剂量为 IΔ t/( Seq),其中 e ≈ 1.6×10 –19 C, q是离子的电荷态。对注入面积,以前实验是通过目测束斑打到石英片上的发光范围来确定。这种方法确定的面积准确度不高,尤其是当注入面积比较小时,可能给注入剂量带来较大误差,例如对于10 mm×10 mm,若长宽各差0.5 mm,则将给注入剂量带来最大约10%的误差。
测量流强可以通过法拉第杯,再结合束流积分仪来得到积累的电荷量。若要得到束流强度的准确结果,不仅需要周密设计法拉第杯的结构,在测量线路上也需要加以考虑。McKenna [ 16- 17] 对强流离子束注入中的剂量测量问题进行了详细论述,指出了几种常规法拉第杯结构的优缺点(我们曾用过与文献[ 17]中图10类似的杯结构),强调了次级电子抑制电极的电流需要进入束流积分电路中。此外,四法拉第杯的方式也广泛用于离子注入过程中 [ 18- 19] 。该方法是在样品前方四角放置四个小法拉第杯,束流均匀扫描区域需要覆盖四个法拉第杯的位置,从而测得流强,显然这种方法束流扫描的幅度需要很大。由于本加速器主要提供MeV量级的离子,相对于离子注入机等设备流强较弱,我们根据束线结构设计了安装方便、电路简洁、测流准确的直接式与间接式法拉第杯结构。
2.3 直接式与间接式法拉第杯的设计
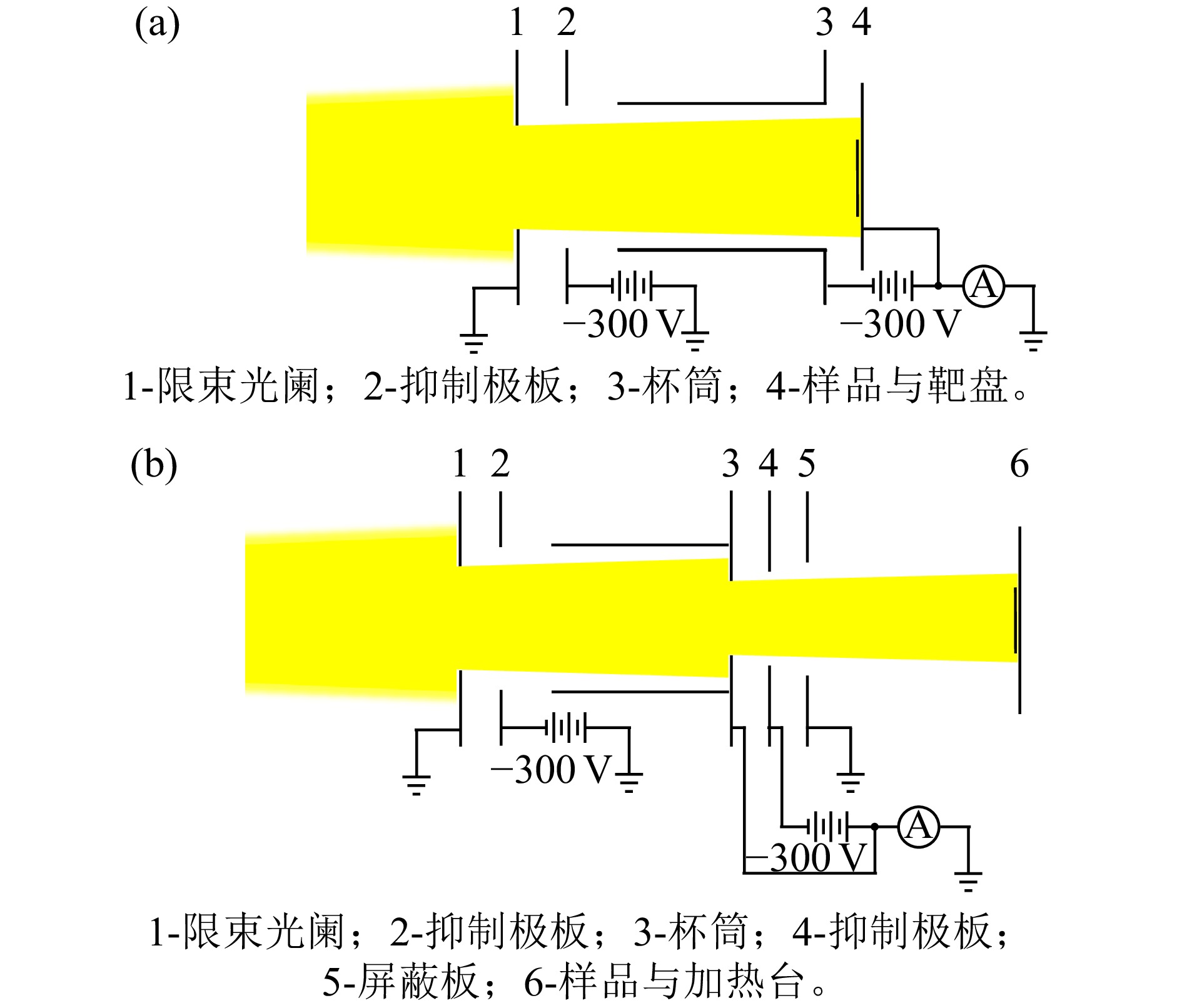
束流轰击在靶盘上,会产生大量次级粒子,包括次级电子和次级正、负离子等。其中主要成分是次级电子,当入射离子比较重时,次级正离子的影响不可忽略 [ 20] 。为了提高了注入剂量的精确度,对室温注入,设计了一种直接式的法拉第杯结构,在均匀注入的前提下束流利用率可达最大。该法拉第杯位于小靶室内,其结构如 图3(a)所示。限束光阑接地,用来控制扫描尺寸,使均匀扫描部分通过光阑打到靶盘上。由于扫描束流具有一定角度,实际辐照尺寸比光阑尺寸略大,可在靶盘处放置坐标纸,根据束流扫描痕迹测出实际辐照尺寸。杯筒接–300 V电压,靶盘上生成的次级电子会被抑制,但是次级正离子会打到杯筒上,如果这部分电荷没有进入束流积分仪,测到的流强会比实际流强偏小,因此,靶盘与杯筒的电流信号需一起接入束流积分仪。此外,束流打到限束光阑上也会有次级电子和次级正离子产生,尤其是束流打在光阑边框上时,次级正离子会在电场的作用下打到杯筒上,将对束流强度测量带来影响。为了避免次级正离子对束流测量的影响,在限束光阑与杯筒间加一块金属抑制板,接–300 V电压。
对于高温辐照,束流测量目前采用两种方法,其一是在样品前放置一个可移动的法拉第杯,每隔一段时间将法拉第杯移动到样品正前方,使束流完全进入杯中,从而测量束流强度,根据该时间段的平均流强计算注入剂量,累积达到需要的剂量值。这种方法对于束流强度比较稳定或一段时间内流强线性变化时的测量比较准确。由前述可知,要计算注入剂量值,不仅需要知道流强,还需要知道束流扫描面积,此时可以通过观察束流打在石英片上的束斑范围来确定扫描尺寸。如前所述,这种方法对面积的确定往往不够精确,因此对剂量值的计算可能会带来较大误差。
为了进一步提高注入剂量的准确性,设计了一种间接式法拉第杯,如 图3(b)所示。结构与室温辐照的法拉第杯类似,但更复杂一些。扫描后的束流通过限束光阑进入杯中;杯筒底部光阑尺寸比限束光阑略小,由于进入限束光阑的束流密度是均匀的,因此测量被杯筒挡住部分的束流就可以间接得到通过杯筒的束流强度,即为打到样品上的流强。为了防止束流打在杯筒光阑边框处产生的次级电子和次级正离子从后面逃逸,在杯筒后面加了抑制极板,其上加–300 V电压,与杯筒一起接入束流积分仪。由于法拉第杯与加热台距离比较近,约7 cm,为防止束流打在样品上产生的次级电子和正离子对束流测量带来影响,在法拉第杯后面加了一块接地的金属板作为屏蔽板。设通过限束光阑打到杯筒上的束流面积为 S 1,杯筒底部光阑孔的面积为 S 2,则被挡住部分面积为 S 1– S 2,测得其流强为 I 1。所以通过杯筒的束流强度 I= I 1× S 2 /( S 1– S 2)。轰击在加热台上的束流面积 S 3由杯筒底部光阑限制。因此,样品的注入剂量可以准确得到。需要注意的是,计算注入剂量时用到的面积 S 1, S 3都要比光阑边框尺寸略大,可用坐标纸测量其面积。
3. 实验测试与结果
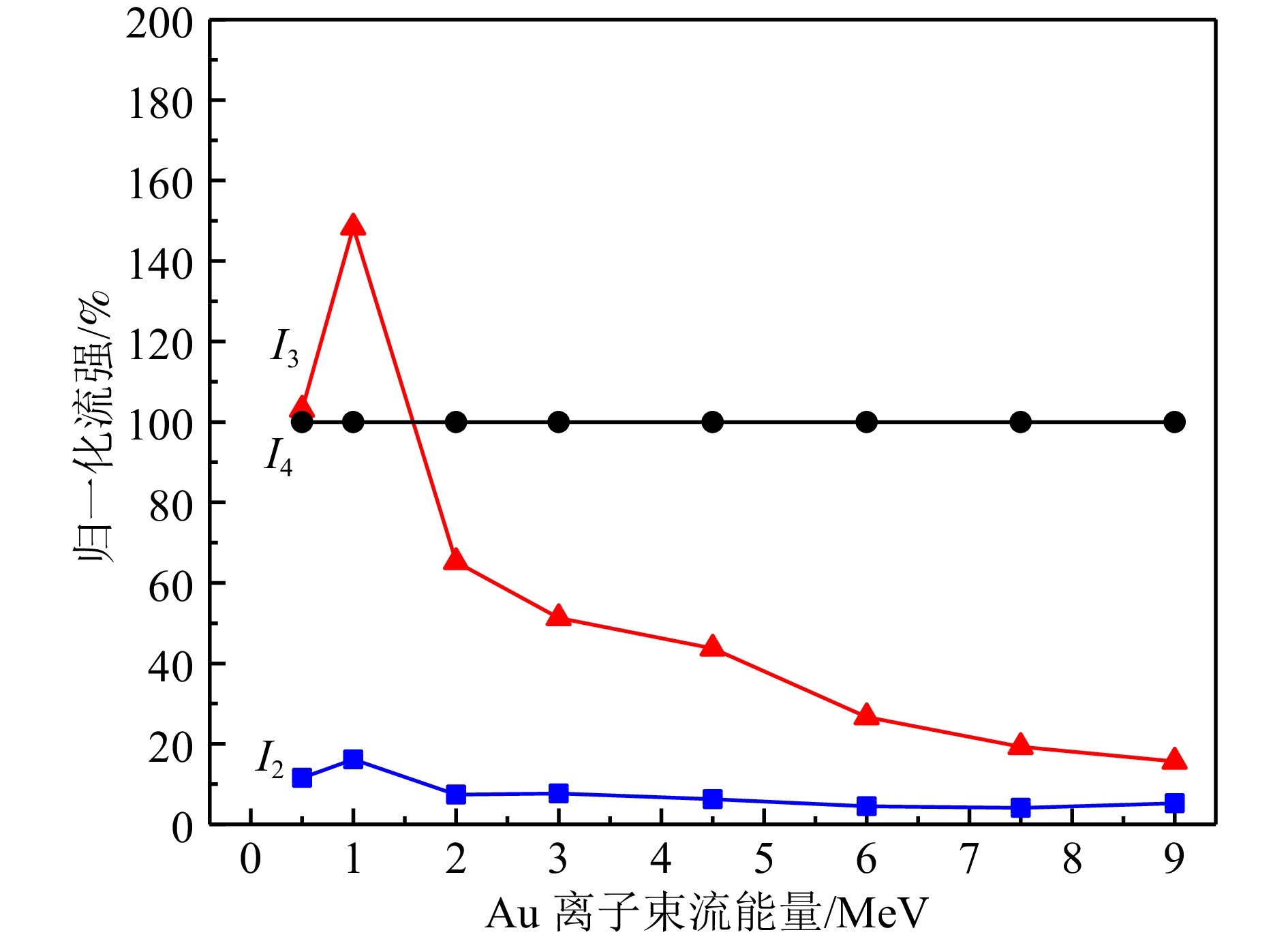
以直接式法拉第杯为例,当0.5~9.0 MeV的Au离子轰击靶盘(圆槽中仅放有铜片)时,利用中国科学院应用物理研究所研制的89型束流积分仪测量了抑制极板、杯筒和靶盘上的电流 I 2, I 3和 I 4。测试时,抑制极板和杯筒上一直加有–300 V电压,因此测到的电流是由次级正离子引起的。测试结果如 图4所示,为了便于比较,进行了归一处理,将靶盘上的电流 I 4设为100%。可见,对于较低能量的Au离子轰击铜片,在杯筒上收集到的次级正离子引起的电流与靶盘上的电流大小相当,并且随束流能量升高而降低。此外,在相同实验设置下测试了比Au离子轻很多的C离子的情况,在1~4 MeV能量范围内, I 3/ I 4的比例在3%左右。
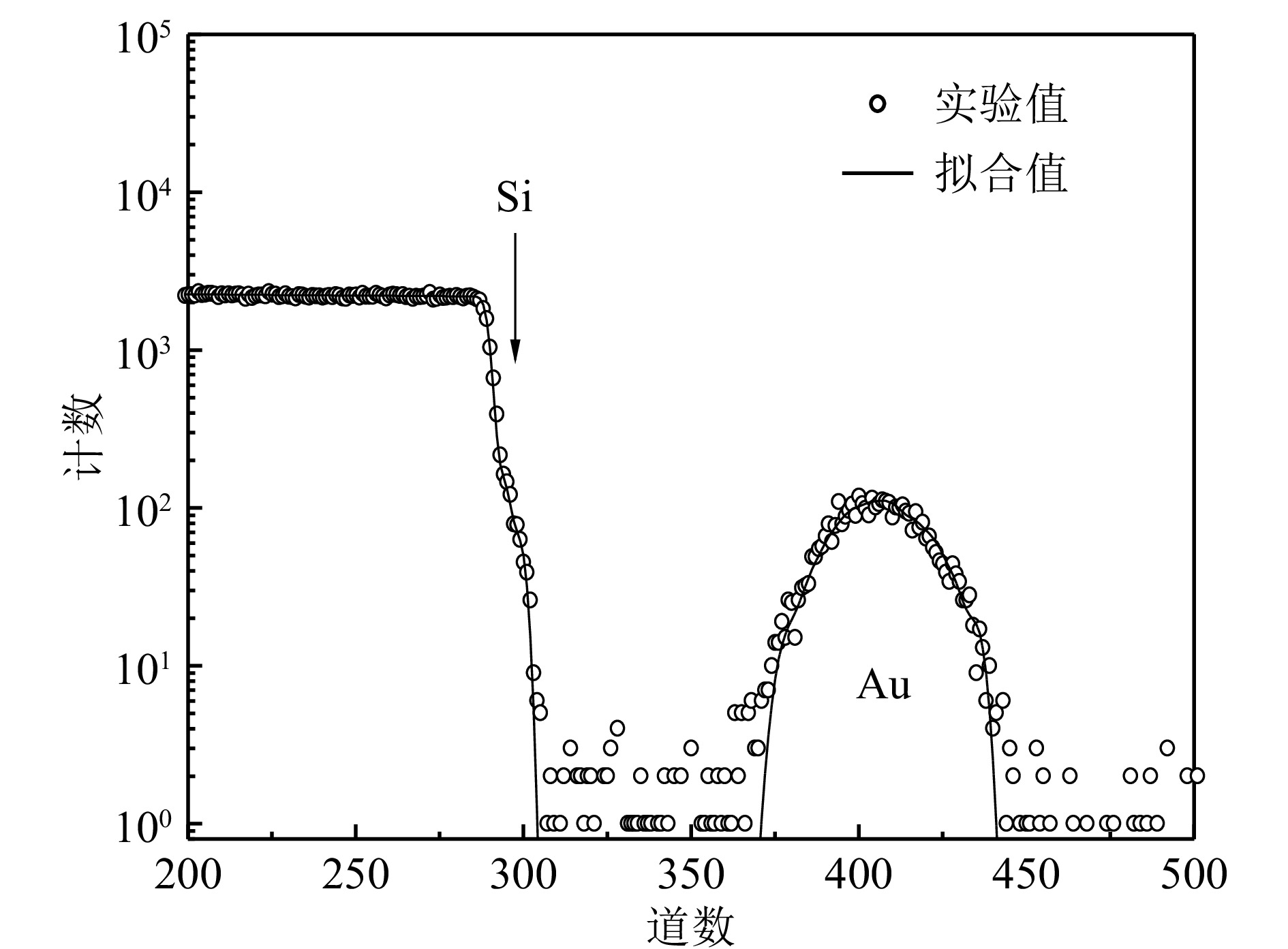
为了检验上述两种法拉第杯的实际使用效果,分别利用几种常用能量的Au离子在10 mm×10 mm的单晶Si片上进行了注入实验。实验后利用RBS方法对注入剂量进行了测量 [ 21- 22] 。入射束流为He 2+离子,能量采用3.0或3.8 MeV,使注入的Au离子信号峰与Si衬底信号分开,避免重叠,便于数据分析。束流沿样品法线入射,在散射角为160°方向用钝化注入平面硅(Passivated Implanted Planar Silicon (PIPS))探测器探测散射的He粒子,探测器的分辨率约为20 keV。在靶盘上加+300 V电压抑制次级电子, 4He 2+流强约10 nA,死时间小于1%,入射离子的总电荷量为8.5 μC。为了得到精确的实验结果,利用SIMNRA7.01软件对各实验谱进行了模拟分析 [ 23] ,其中电子阻止本领数据采用了KKKNS参数,其精度为2% [ 24- 25] 。典型模拟谱如 图5所示,模拟谱与实验谱符合得很好,模拟结果准确可靠。在每块样品的上下左右四个位置各做了测试,其平均剂量作为最终测量剂量。 表1列出了直接式法拉第杯与间接式法拉第杯应用于离子注入实验的测试结果。测量剂量的误差主要来自Au峰的统计误差 (约为1.4%,对于注入剂量为5.0×10 15 cm –2)、散射角偏差(约为1.22%)以及阻止本领(精度约为2%)。可见,测量剂量与期望剂量的误差在4%以内,效果很好,满足注入实验的要求。
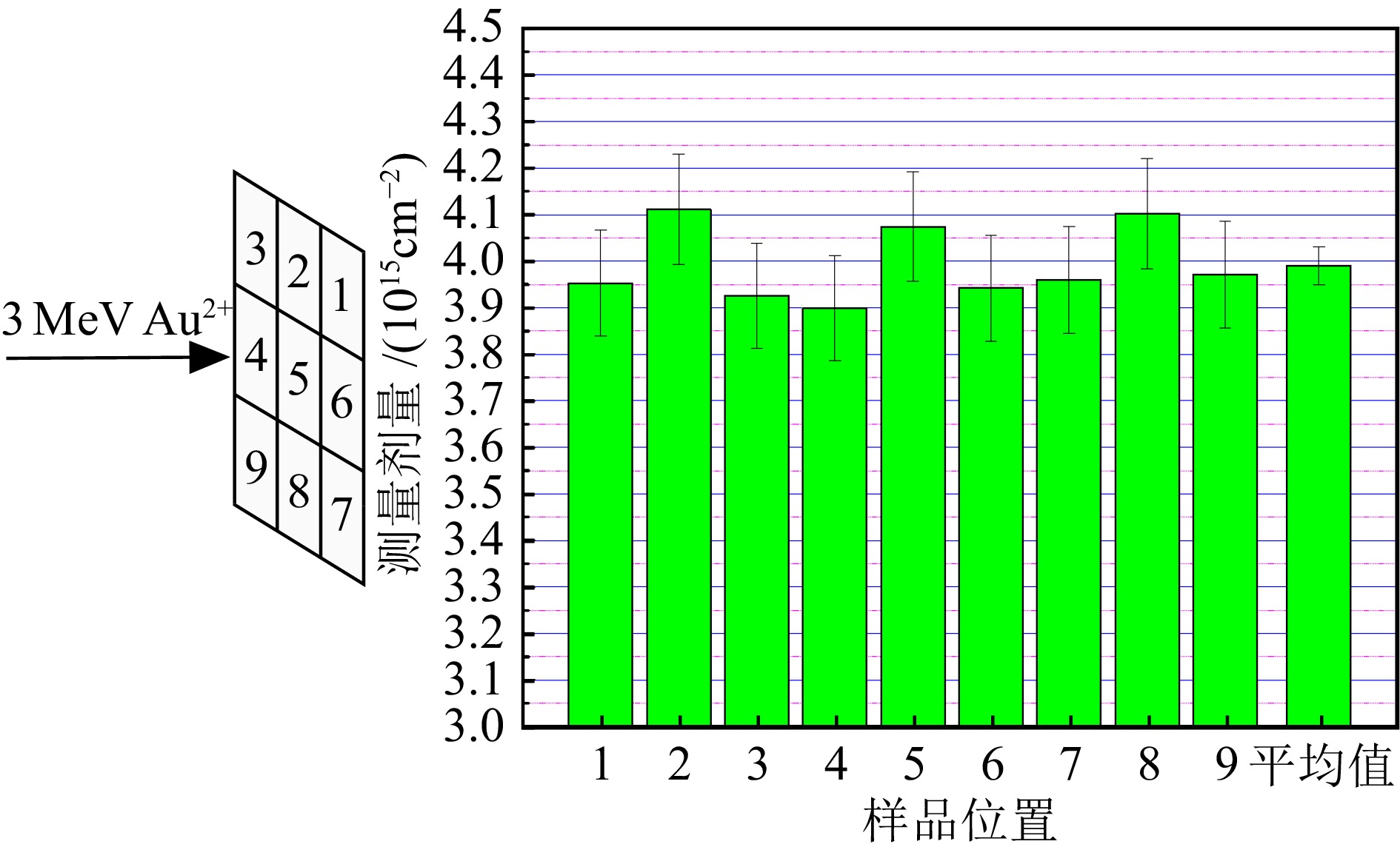
表 1 对于直接式与间接式法拉第杯结构,RBS测量注入剂量与期望注入剂量的比较能量/MeV 离子 直接式法拉第杯 间接式法拉第杯 期望剂量/(10 15 cm –2) 测量剂量/(10 15 cm –2) 误差/% 期望剂量/(10 15 cm –2) 测量剂量/(10 15 cm –2) 误差/% 0.5 Au + 1.5 1.55(3) 3.3 — — — 1.0 Au + 5.2 5.36(7) 3.1 — — — 3.0 Au 2+ 5.0 5.09(7) 1.8 3.0 2.97(5) –1.0 6.0 Au 3+ 3.0 3.11(5) 3.7 3.5 3.50(6) 0 由于室温注入系统的辐照面积较大,为了检验注入的均匀性,利用3 MeV的Au 2+在20 mm×20 mm的Si片样品上进行了注入实验,期望剂量为4.0×10 15 cm –2。为了尽量减小管道中残余气体对注入均匀性的影响,实验过程中靶室真空约1.1×10 –4 Pa。注入实验结束后,在Si片样品上的9个位置进行RBS测试分析,测量各位置的注入剂量。结果如 图6所示,9个位置的测量剂量相近,平均值为(3.99±0.04)×10 15 cm –2,与期望剂量相差0.25%,相对标准偏差(注入剂量的均匀性)为2%,满足注入实验的要求。
4. 小结
北京大学1.7 MV串列静电加速器可将从H到Au的大部分元素的离子加速至几百keV到若干MeV的能量,能够进行离子注入/辐照实验,以及RBS和沟道分析等离子束分析工作。在原有室温注入基础上,建立了高温辐照系统,温度最高可达950 ℃。为了实现更加精确的离子注入,设计了直接式与间接式两种法拉第杯结构,扫描面积可以精确控制,在测量流强时除了抑制次级电子,还考虑到了次级正离子的影响。RBS分析显示测量剂量与期望剂量误差在4%以内。此外,注入均匀性的测试表明注入剂量的相对标准偏差为2%。
-
表 1 对于直接式与间接式法拉第杯结构,RBS测量注入剂量与期望注入剂量的比较
能量/MeV 离子 直接式法拉第杯 间接式法拉第杯 期望剂量/(10 15 cm –2) 测量剂量/(10 15 cm –2) 误差/% 期望剂量/(10 15 cm –2) 测量剂量/(10 15 cm –2) 误差/% 0.5 Au + 1.5 1.55(3) 3.3 — — — 1.0 Au + 5.2 5.36(7) 3.1 — — — 3.0 Au 2+ 5.0 5.09(7) 1.8 3.0 2.97(5) –1.0 6.0 Au 3+ 3.0 3.11(5) 3.7 3.5 3.50(6) 0 -
[1] WANG Peipei, WANG Xingjun, DU Jinlong, et al. Acta Materialia, 2017, 126: 294. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2016.12.018
[2] WANG Peipei, XU Chuan, FU Engang, et al. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 440: 396. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.01.072
[3] DU Jinlong, CHEN Huaqiang, XU Chuan, et al. Acta Materialia, 2021, 210: 116798. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116798
[4] DU Jinlong, QIU Yuanhang, ZHANG Jian, et al. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 465: 1014. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.09.174
[5] LIANG Yanxia, DU Jinlong, XU Chuan, et al. Intermetallics, 2019, 114: 106608. DOI: 10.1016/j.intermet.2019.106608
[6] WU Zaoming, ZHANG Jun, ZHANG Jian, et al. Nuclear Fusion, 2019, 59: 106050. DOI: 10.1088/1741-4326/ab34c8
[7] WANG Jing, HU Zhaoyi, LI Rui, et al. Nanotechnology, 2018, 29: 184001. DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/aab005
[8] HU Zhaoyi, CHEN Huaqiang, ZHAO Yunbiao, et al. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 843: 155829. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155829
[9] HU Zhaoyi, XU Chuan, LIANG Yanxia, et al. Scripta Materialia, 2021, 190: 136. DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.042
[10] CAO Peipei, WANG Hui, HE J Y, et al. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 859: 158291. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.158291
[11] SUN Yingjun, LIANG Yanxia, LUO Mingchuan, et al. Small, 2018, 14: 1702259. DOI: 10.1002/smll.201702259
[12] LIANG Yanxia, SUN Yingjun, WANG Xinyu, et al. Nanoplate, 2018, 10: 11357. DOI: 10.1039/c8nr02527d
[13] SUN Cheng, WANG Peipei, WANG Hao, et al. Nano Research, 2019, 12: 1613. DOI: 10.1007/s12274-019-2400-1
[14] HU Zhaoyi, WANG Jing, LI Rui, et al. Langmuir, 2018, 34: 13041. DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b02764
[15] LI Shuyao, FAN Yong, CHEN Huaqiang, et al. Energy & Environmental Science, 2020, 13: 896. DOI: 10.1039/c9ee03307f
[16] MCKENNA C M. Radiation Effects, 1979, 44: 93. DOI: 10.1080/00337577908245983
[17] MCKENNA C M. Faraday Cup Designs for Ion Implantation[C]// RYSSEL H, GLAWISCHNIG H eds. Ion Implantation Technique. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 1982: 73.
[18] JIMÉNEZ-REY D, BENEDICTO M, MUÑOZ-MARTÍN A, et al. Nucl Instr and Meth B, 2014, 331: 196. DOI: 10.1016/j.nimb.2014.01.030
[19] HAN Jifeng, AN Zhu, ZHENG Gaoqun, et al. Nucl Instr and Meth B, 2018, 418: 68. DOI: 10.1016/j.nimb.2018.01.002
[20] JAMBA D M. Rev Sci Instrum, 1978, 49: 634. DOI: 10.1063/1.1135473
[21] 赵国庆. 理化检验-物理分册, 2002, 38(1): 41. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4012.2002.01.014 ZHAO Guoqing. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis part A:Physical Testing, 2002, 38(1): 41. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4012.2002.01.014
[22] NASTASI M, MAYER J W, WANG Y. Ion Beam Analysis: Fundamentals and Applications[M]. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 2015: 70.
[23] MAYER M. Nucl Instr and Meth B, 2014, 332: 176. DOI: 10.1016/j.nimb.2014.02.056
[24] KONAC G, KALBITZER S, KLATT C, et al. Nucl Instr and Meth B, 1998, 136-138: 159. DOI: 10.1016/S0168-583X(98)80016-5
[25] BIANCONI M, ABEL F, BANKS J C, et al. Nucl Instr and Meth B, 2000, 161-163: 293. DOI: 10.1016/S0168-583X(99)00927-1
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 徐川,付恩刚,高原,任晓堂. 北京大学静电加速器及其应用. 科学通报. 2023(09): 1096-1103 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 徐川,付恩刚,楼建玲. 背散射方法测薄膜厚度和杂质分布. 物理实验. 2022(03): 10-16+21 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载:
 甘公网安备 62010202000723号
甘公网安备 62010202000723号